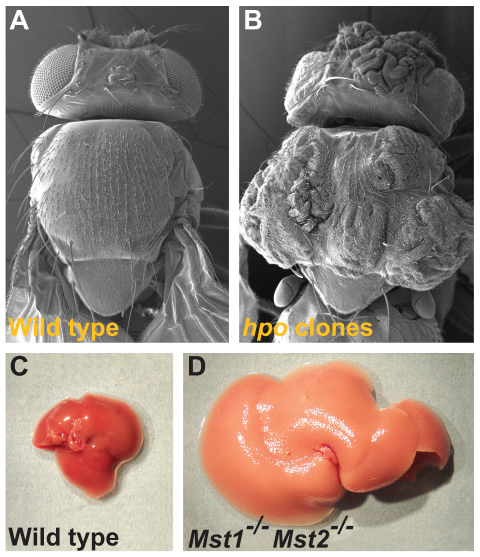
Fig. 1.
Hippo mutant phenotypes in flies and mice. (A,B) Scanning electron micrographs of (A) a wild-type fly and (B) a fly with clones of cells homozygous mutant for hippo that exhibit overgrowth of the adult cuticle (Udan et al., 2003). (C) A mouse liver at 2 months of age from a wild-type animal and (D) a liver at 2 months of age from a mouse mutant in which both Mst1 and Mst2 (Stk3 and Stk4), two mammalian Hippo homologs, have been conditionally inactivated in the developing liver (Lee et al., 2010; Lu et al., 2010; Song et al., 2010; Zhou et al., 2009). The double null Mst1/2 mutant liver is overgrown owing to an increase in cell numbers.