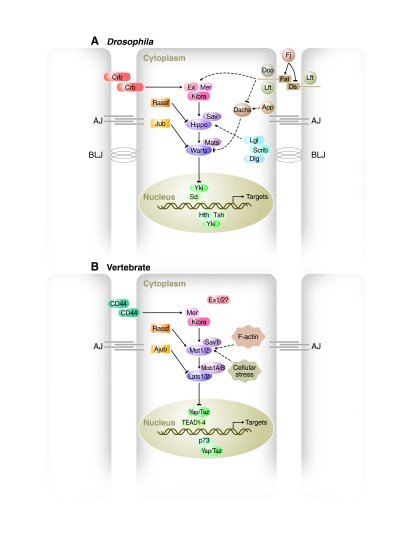
Fig. 2.
Schematics of the Hippo pathway in flies and mice. Cells (outlined in grey, nuclei in green) are shown with adherens junctions (AJ) and basolateral junctions (BLJ). (A,B) Hippo pathway components in (A) Drosophila and (B) vertebrate are shown in various colors, with pointed and blunt arrowheads indicating activating and inhibitory interactions, respectively. Continuous lines indicate direct interactions, whereas dashed lines indicate unknown mechanisms. See text for further details. Abbreviations: Ajub, Ajuba; App, Approximated; Crb, Crumbs; Dco, Discs overgrown; Dlg, Discs large; Ds, Dachsous; Ex, Expanded; Fj, Four-jointed; Hth, Homothorax; Jub, Drosophila Ajuba; Lats, Large tumor suppressor; Lft, Lowfat; Lgl, Lethal giant larvae; Mer, Merlin; Mats, Mob as a tumor suppressor; Mob1A/B, Mps1 binder; Mst, Mammalian sterile 20 like; Rassf, Ras-associated factor; Sav, Salvador; Scrib, Scribble; Sd, Scalloped; Taz, transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif; TEAD, TEA domain protein; Tsh, Teashirt; Yap, Yes associated protein; Yki, Yorkie.