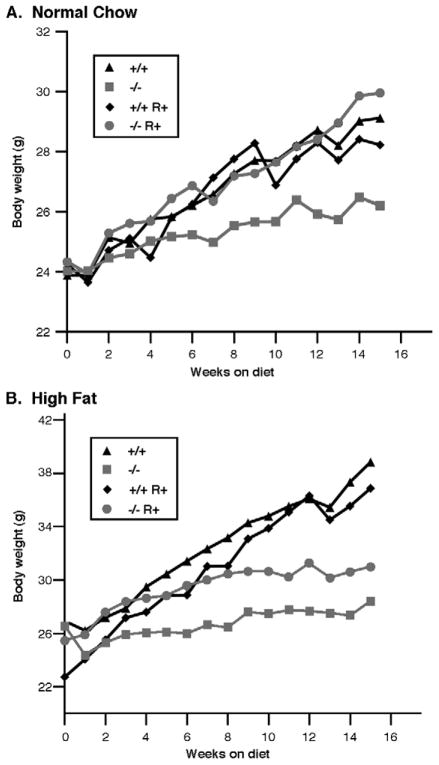
Figure 1.
Body weight gain of animals treated with rosiglitazone on either a normal chow diet (A) or a high fat diet (B). Female animals (WT, +/+ or HSL null, −/−) of 12 week old were randomized to NC (normal chow), NC+R (normal chow supplemented with rosiglitazone), HF (high fat), and HF+R (high fat supplemented with rosiglitazone) diets ad libitum for 16 weeks (n=8 in each group). Body weights were measured each week; data presented are the average of eight animals per group.