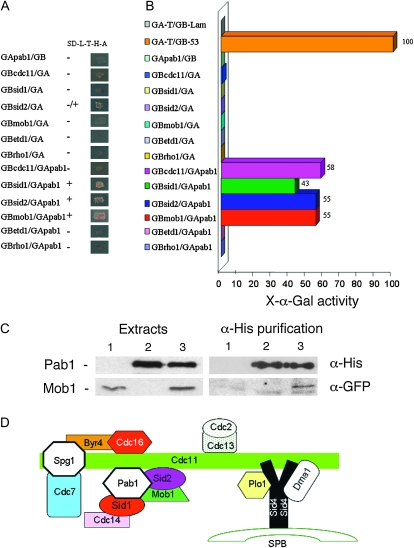
Figure 5.—
Physical interaction between Pab1 and SIN proteins. (A) Protein–protein interactions were examined using the yeast two-hybrid system. S. cerevisiae AH109 cells transformed with Gal4-binding domain-fused and Gal4 activation domain-fused genes were grown on SD without leucine, tryptophan, histidine, and adenine. (B) Interactions were also tested using a colorimetric assay to test for α-galactosidase activity. The constructions GA-T/GB-Lam and GA-T/GB-53 were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. (C) Western blot analysis of Pab1 (MycHis-pab1construct) and Mob1 (mob1-GFP construct) with anti-α-His and anti-α-GFP antibodies, respectively. Yeast extracts were purified using immobilized cobalt affinity from a Mob1-GFP strain expressing Myc6His-Pab1 protein from a plasmid. Lane 1: mob1-GFP strain; lane 2: wild-type strain expressing pREPMycHis-pab1; and lane 3: mob1-GFP strain expressing pREPMycHis-pab1. In lane 3, Mob1-GFP is copurified with Pab1 protein. (D) Model for the physical assembly of different SIN components and regulators in the SPB from Morrell et al. (2004). The Sid2-Cdc14 complex is shown to interact with Pab1.