Fig. 2.
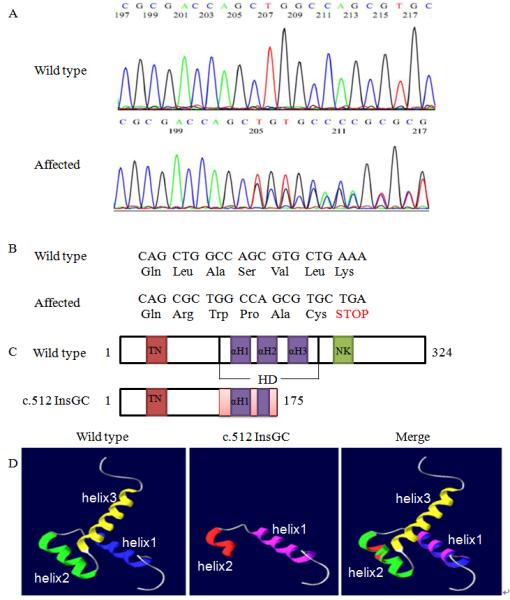
Identification of a novel NKX2.5 mutation, c.512InsGC, in the family with CHD. A: Sequencing results from one normal family member (WT) and one patient (c.512InsGC). B: Schematic diagram showing the frame-shift effect caused by the c.512InsGC mutation. C: Structure of the NKX2.5 protein and the effect of the c.512InsGC mutation. NKX2.5 contains 324 amino acids with a TN domain (amino acids 10-21), a HD with three α-helices (139-197) and a NK2-SD domain (210-233). HD αH1, 147-159; αH2, 165-175; αH3, 179-195. D: The three-dimensional structure of the NKX2.5 HD domain. For wild type NKX2.5, the three α-helices are indicated by different colors, blue, green, and yellow, respectively. For mutant NKX2.5 generated by c.512insGC, the pink color indicates α-helix 1 and red shows α-helix 2. The merged diagram indicates that the mutant NKX2.5 lost the second half of the α-helix 2 and entire α-helix 3.
