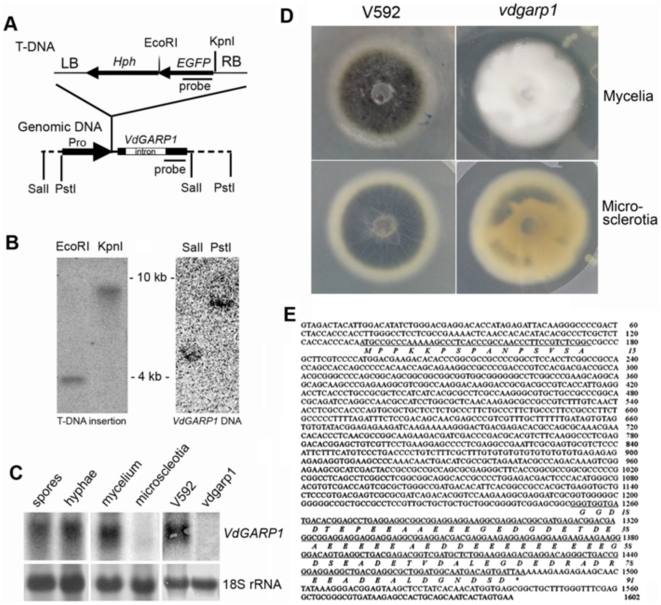
Figure 3. Characterization of VdGARP1 gene.
(A) Schematic diagrams of T-DNA and VdGARP1 genomic DNA construct. T-DNA insertional position upstream 358 bp from initiation codon in VdGARP1 genomic was shown. (B) DNA gel blot analysis of T-DNA insertional copy number from vdgarp1 mutant (left panel), and VdGARP1 DNA copy number from V592 (left panel) with 32P-labeled T-DNA-specific or VdGARP1-specific DNA probe shown in (A). (C) Identification of expression of VdGARP1 mRNA in spores, hyphae, mycelia and microscleotia of V592, as well as in mycelia of V592 and vdgarp1 mutant, with 32P-labeled VdGARP1-specific DNA probe shown in (A). rRNAs stained with methylene blue trihydrate were used as a loading control. (D) Morphology of V592 and vdgarp1 colony. vdgarp1 mutant displayed denser appearance mycelia with great delayed and reduced microsclerotial development on PDA agar medium compared to that of V592. (E) Full length VdGARP1 cDNA sequence obtained by 5′-rapid amplification of cDNA end (5′RACE) and 3′RACE, revealing VdGARP1 gene encodes an glutamic acid-rich protein from a gene with a 1076 bp intron sequence.