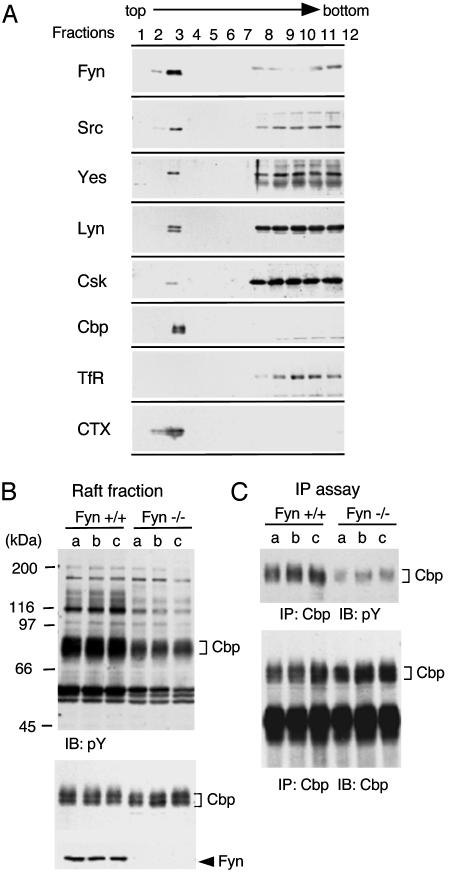
Fig. 1.
(A) Localization of SFK-related proteins in lipid rafts. Neonatal mouse brains were homogenized in a buffer containing 1% Triton X-100, and the raft fractions were separated on a discontinuous sucrose gradient. The fractions (1 ml) were collected from the top of the gradient and subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies against indicated proteins. Transferrin receptor and B-subunit of cholera toxin-reactive ganglioside GM1 were detected as a marker of non-raft membrane protein and a marker of lipid rafts, respectively. (B) Tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in lipid rafts from wild-type and Fyn-deficient mouse brain. Lipid raft fractions were prepared from three littermates (a, b, and c) of wild-type (fyn+/+) and Fyn-deficient (fyn–/–) mice and immunoblotted with anti-phosphotyrosine (pY) (Top), anti-Cbp (Middle) and anti-Fyn (Lower) antibodies. Positions of molecular mass markers are shown on the left of the blots. (C) Tyrosine phosphorylation of Cbp from wild-type and Fyn-deficient mouse brain. Cbp was immunoprecipitated (IP) from lipid raft fractions, and the immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with anti-pY (Upper) and anti-Cbp (Lower) antibodies.