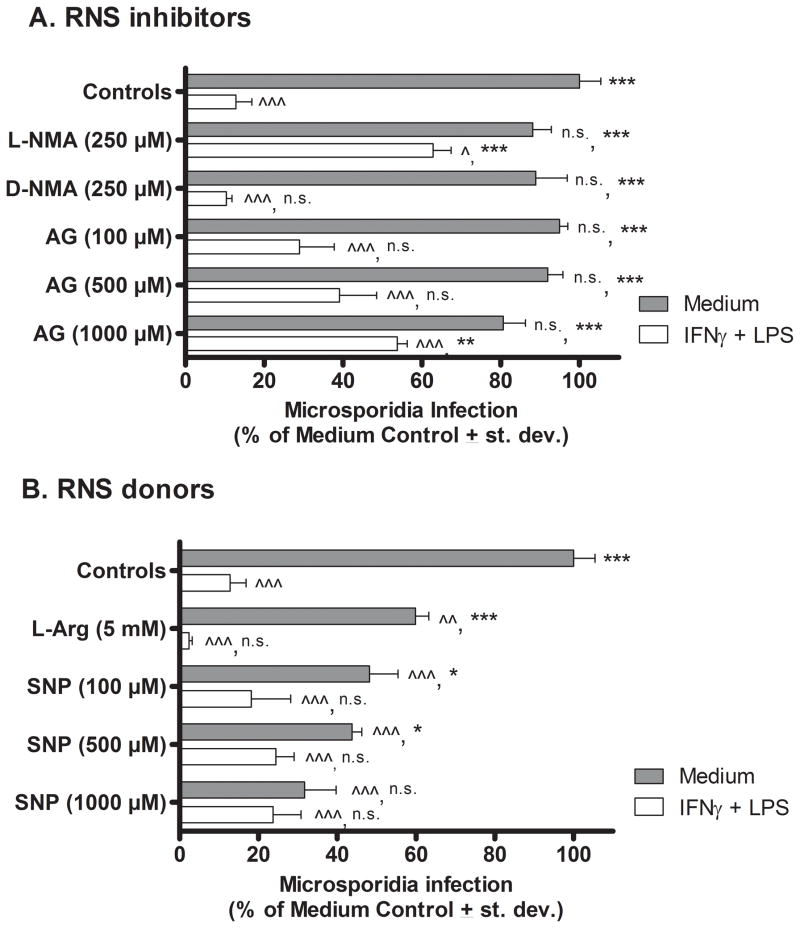
Figure 1.
Effect of RNS inhibitors and donors on E. cuniculi replication in murine peritoneal macrophages in vitro. Cultures of WT mouse PEC macrophages were treated with medium (filled bars) or activated with IFNγ plus LPS (open bars), inoculated with E. cuniculi, and treated with RNI inhibitors (Panel A) or donors (Panel B). Three days later (72 hrs), the cultures were fixed and stained. Microsporidia were counted per 100 macrophages and results were calculated as percent of infected medium control (non-activated) macrophages (i.e. microsporidia per 100 medium-treated control macrophages = 100%). ANOVA was used to compare results of experimental groups against microsporidia infectivity in resting medium-treated control macrophages (denoted by ^ in the first position) and against activated (LPS + IFNγ-treated) control macrophages (denoted by * in the second position). Statistically significant differences were designated; ^ or * as P < 0.05; ^^ or ** as P < 0.01; ^^^ or *** as P < 0.001; n.s. = not significant.