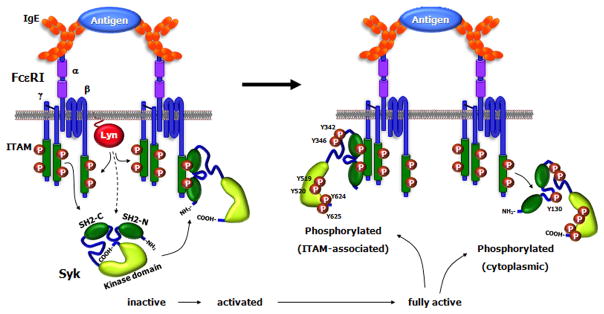
Fig 2.
Syk Activation. The globular representation of Syk shows the molecule in its autoinhibitory state with the COOH-terminal tail interacting with the inter-SH2 domains thereby contributing to keeping the molecule in a closed conformation. The binding of Syk to the phosphorylated ITAM results in a conformational change that exposes the COOH-terminal region. This leads to the phosphorylation of two tyrosines in the tail, which then keeps the molecule in an open conformation allowing for further phosphorylation of other tyrosine residues mostly by autophosphorylation, although there could be contributions by other tyrosine kinases. Phosphorylation of Tyr-130 in the inter-SH2 domain results in Syk dissociating from the ITAM.