Figure 3.
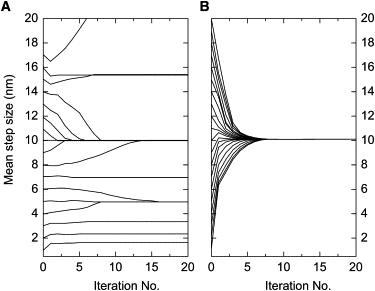
Sensitivity to initial guesses of step size. Analysis of a 200-point time course with HMM algorithms. The simulation had Gaussian-distributed step sizes of 10 ± 1 nm, mean dwell time of 8 and noise σ = 2 nm, chosen to match the simulations in Milescu et al. (14). Initial guesses of step size were Gaussian distributions with mean values of 1 to 20 nm, with standard deviations of 2 nm. The estimated mean step size is plotted as a function of iteration number. (A) Results of the HMM algorithm of Milescu et al. (14), reproduced from their Fig. 7B. Only starting distributions with means between 8 and 14 nm result in convergence to the correct step size. (B) Convergence of step-size estimates from the one-state VS-HMM algorithm described in this article, employing Gaussian-constrained reestimation (Eq. 23) to allow a direct comparison. Convergence is reliable with initial guesses throughout the range of 1–20 nm.
