Figure 5.
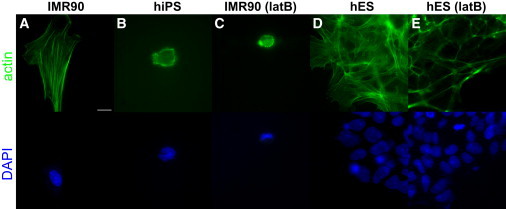
Actin microfilaments confer elasticity to differentiated parental fibroblasts and hES cells. (A and B) IMR90 fibroblasts and hiPS cells exhibit significantly different microfilament architecture. IMR90 cells contain a rich internal microfilament network typical of cultured fibroblasts, whereas hiPS cells are largely devoid of internal actin filament structure, such as filament bundles, reminiscent of the undifferentiated C. elegans zygote (7). (C) Depolymerization of actin filaments by latB in IMR90 cells led to a marked decrease in their elasticity down to values found for hiPS cells. (D) Colonies of hES cells show a rich basal actin microfilament structure, similar to that of IMR90 cells. (E) LatB treatment of hES cells largely depolymerized the intracellular actin network, whereas cortical actin structures remained intact. Scale bar, 20 μm.
