Figure 5.
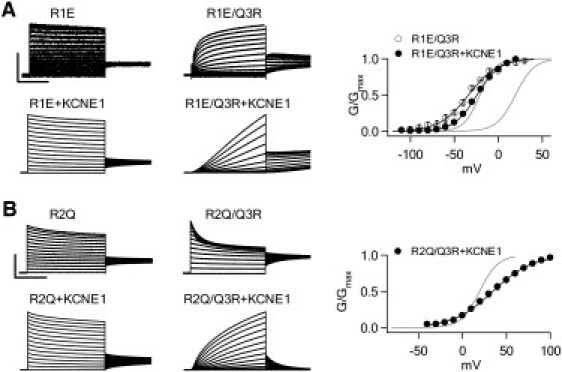
Charge addition to Q3 rescues voltage dependence in charge reduction mutations to R1 and R2. (A) Currents and G-V relationship from R1E and R1E/Q3R. Q3R restores voltage dependence to R1E in both the absence and presence of KCNE1. Voltage pulses of 5 s duration ranged from −80 to 60 mV in 10 mV increments for activating R1E-/+KCNE1 currents, and from −120 to 20 mV for R1E/Q3R-/+KCNE1 currents. The holding and repolarizing potentials were −80 mV for 32 s and −40 mV for 3 s, respectively. Scale: R1E 1 μA, R1C/Q3R 1.5 μA, R1E+KCNE1 25 μA, R1E/Q3R+KCNE1 10 μA; 2 s. (B) Currents and G-V relationship from R2Q and R2Q/Q3R. Q3R only restores voltage dependence to R2Q in the presence of KCNE1. Voltages ranged from −80 to 60 mV for activating R2Q-/+KCNE1 and R2Q/Q3R currents, and from −40 to 100 mV for R2Q/Q3R+KCNE1 currents. Scale: R2Q 2 μA, R2Q/Q3R 5 μA, R2Q+KCNE1 40 μA, R2Q/Q3R+KCNE1 15 μA; 2 s. In the G-V plots of both A and B, the black curves are fittings of the Boltzmann equation to the mutants, and the gray curves are the G-V relations of WT Kv7.1 (left) and Kv7.1+KCNE1 (right).
