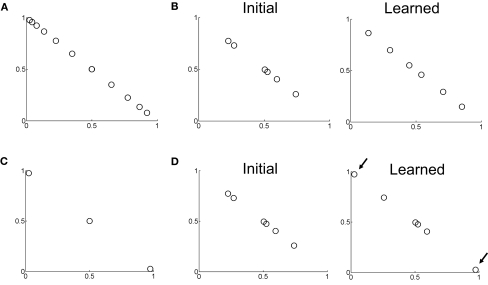
Figure 10.
Learning of belief basis functions in the model. (A) Samples of input beliefs for a set of trials where motion coherence was set to 30%. (B) (Left) Initial randomly selected basis belief points in the network (input to hidden layer weights). (Right) Belief basis points learned by the network for predicting value for the belief distribution in (A). Note that learning has caused the belief points to spread out so as to sufficiently capture the input belief distribution shown in (A) to predict value. (C) Distribution of input beliefs when motion coherence is set to 95%. (D) (Left) Initial randomly selected basis belief points (same as in B left panel). (Right) Basis belief points after learning. The arrows indicate the two belief points that underwent the most change from their initial values – these now lie at the two extremes to better approximate the input distribution of beliefs in (C) and more accurately predict value.