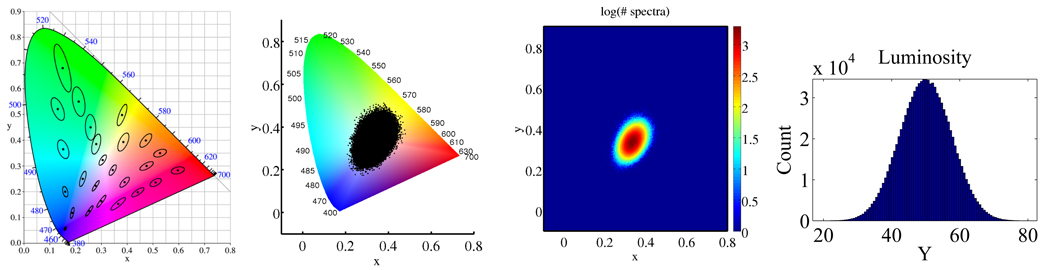
Fig. 1.
Left: MacAdam ellipses in the CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram. Each ellipse is shown as 10 times is actual size. Colors within each ellipse are indistinguishable from the color in the center. 2nd from left: 106 random, independent spectra mapped to the chromaticity diagram. 2nd from right: The highly metameric colors are the “least pure” chromaticities, centered around the white point (1/3, 1/3). A color of a pure wavelength (one near the spectral locus) is highly improbable and least likely to be strongly metameric. Right: The luminosity component is normally distributed.