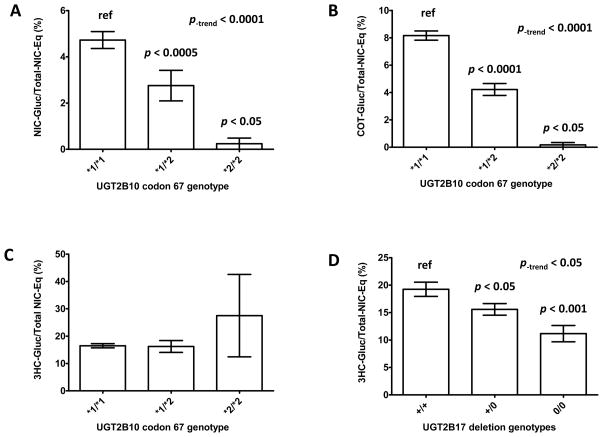
Figure 4. Effect of UGT2B10 and UGT2B17 polymorphisms on nicotine-Gluc, cotinine-Gluc, and 3HC-Gluc levels in urine samples from smokers.
Shown are the percentage of Total-NIC-Eq for urinary nicotine and nicotine metabolite glucuronides for subjects stratified by UGT2B10 codon 67 or UGT2B17 deletion genotypes. Panel A, UGT2B10 genotype vs. urinary nicotine-Gluc; panel B, UGT2B10 genotype vs. urinary cotinine-Gluc; panel C, UGT2B10 genotype vs. urinary 3HC-Gluc; panel D, UGT2B17 genotype versus urinary 3HC-Gluc. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare urine from subjects with the UGT2B10 (*2/*2) or (*1/*2) genotypes to specimens from subjects with the wild-type UGT2B10 (*1/*1) genotype, and the Jonckheere-Terpstra trend test was used to examine the overall effect of UGT genotypes on nicotine-, cotinine-, and 3HC-glucuronide levels determined as a percentage of Total-NIC-Eq. The Students t-test was used to compare urine from subjects with the UGT2B17 (0/0) or (0/+) genotypes to specimens from subjects with the wild-type UGT2B17 (+/+) genotype, and the trend test was performed to examine the overall effect of UGT genotypes on nicotine-, cotinine-, and 3HC-glucuronide levels determined as a percentage of Total-NIC-Eq. Data are shown as the mean ± standard error.