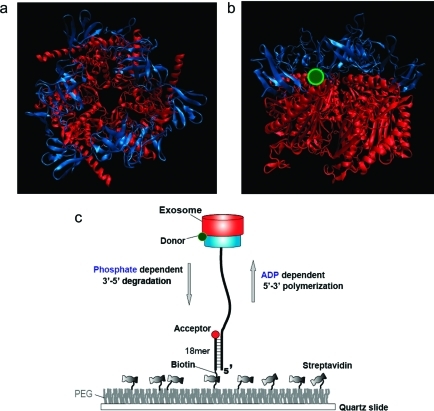
Figure 1.
Archaeal Csl4-exosome and experimental setup. (a) Top-to-bottom view of the crystal structure of the Archaseoglobus fulgidus Csl4-exosome complex (PDB code 2BA1). The protein is composed of nine subunits in which the top three units constitute the RNA binding cap ring (blue) while the bottom six form the catalytic core (red). The double-donut-like structure displays a central channel through which ssRNA enters and is further processed. (b) Side view of the crystal structure. The protein is labeled with a Cy3 fluorophore (green) at the interface between the two rings. (c) An RNA substrate annealed to a DNA strand to form a partial duplex is immobilized to a PEG coated surface via the biotin−streptavidin interaction. The protein complex functions in RNA degradation and polymerization in response to Pi and ADP, respectively. The enzymatic motion can be monitored by the single molecule FRET assay in real time. FRET increases during degradation whereas it decreases during polymerization, serving as a sensitive reporter of the reactions.