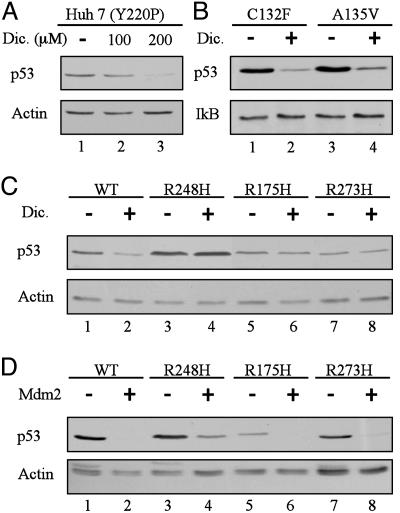
Fig. 3.
p53 mutants R248H, R175H, and R273H are resistant to dicoumarol-induced degradation but sensitive to Mdm2-mediated degradation. (A) Huh 7 cells that carry the Y220P mutant p53 were cultured for 5 h without (-) or with 100 or 200 μM dicoumarol (Dic.). (B) M1 myeloid leukemic cells that carry the C132F or A135V mouse mutant p53 cells were incubated without (-) or with (+) 300 μM dicoumarol for 5 h. (C) HCT116 p53 null cells were transiently transfected with pRc/CMV human wild-type p53 or the p53 mutants R248H, R175H, or R273H. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were cultured for 5 h without (-) or with (+) 300 μM dicoumarol. (D) HCT116 p53 null cells were transiently transfected with pRc/CMV human wild-type p53 or the p53 mutants R248H, R175H, or R273H without (-) or with (+) pCOC-mouse mdm2 × 2. Protein extraction and immunoblot analysis were carried out as described (5) by using mouse monoclonal anti-human p53 (Pab 1801) or anti-mouse and human p53 (Pab 240) antibody. The blots were then stripped and reprobed with mouse monoclonal anti-actin or rabbit anti-IκB antibody.