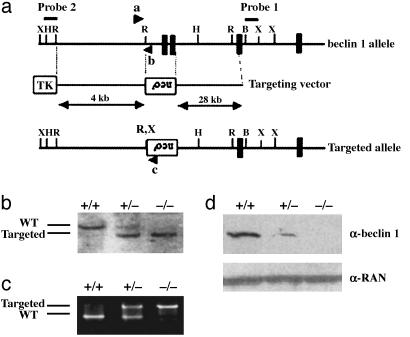
Fig. 1.
Targeted disruption of beclin 1 in embryonic cells. (a) Genomic structure of beclin 1 (showing exons 1–4 only; solid box), targeting vector, and beclin 1 allele after targeted deletion. The start codon is indicated by an asterisk. Arrow ”a” represents a common primer for both the wt and targeted beclin 1 alleles, arrow ”b” represents a specific primer for the wt allele, and arrow ”c” represents a specific primer for the targeted allele. X, XbaI; H, HindIII; R, EcoRI; B, BamHI; neor, neomycin resistance cassette; TK, thymidine kinase marker. (b) Southern blot analysis of beclin 1 mutant ES clones after digestion with XbaI. The probe used to distinguish wt and targeted allele is indicated in a. wt allele is detected at a size of 11 kb, and mutant allele is detected at 7 kb. (c) Competitive PCR assay of three different genotypes of ES cells (+/+, +/-, and -/-) with primers a–c described in a. wt allele (250 bp) can be separated from mutated allele (500 bp) on a 1.5% agarose gel. (d) Western blot study of beclin 1 expression in ES cells from three different genotypes with anti-beclin 1 antibody. Anti-RAN antibody was used for protein loading control in each lane.