Figure 2.
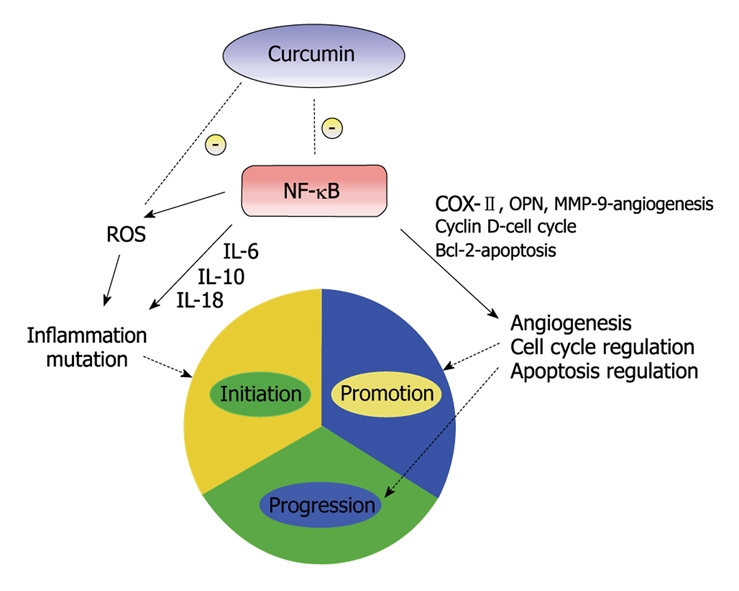
A simplified illustration of curcumin and its effects on the three stages of carcinogenesis. NF-κB has been the subject of research for the development of anti-cancer therapeutic agents due to its effects on multiple stages of carcinogenesis. Curcumin has been shown to prevent phosphorylation and degradation of inhibitor κ B α, thereby blocking NF-κB activation[30]. NF-κB, through multiple pathways, can promote inflammation, angiogenesis and disrupt cell cycle and apoptosis regulation, thus promoting carcinogenesis.
