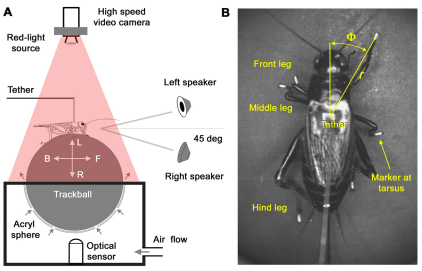
Fig. 1.
(A) A tethered cricket walking on a trackball floating in an air stream. The forward–backward (F–B) and leftward–rightward (L–R) rotations of the trackball were recorded with an optical sensor. The song was presented from either of two speakers placed 45 deg to the left and right of the animal's length axis. A high-speed video camera recorded the cricket's walking movements from above. (B) Markers on the tarsi, head and abdomen were used to measure the cricket's movements. Tarsal trajectories were described by the tarsal distance (r) and tarsal angle (Φ).