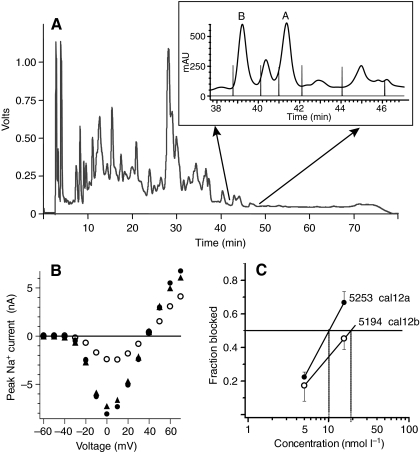
Fig. 4.
Purification of two active toxins from C. californicus crude venom. (A) HPLC chromatogram of crude extract from pooled venom ducts. A fraction collector was used to isolate the doublet at ∼43 min, which was found to have INa-blocking activity. The inset shows the second-stage separation of material eluting in this region, with vertical lines indicating the collection times for individual fractions. Peaks labeled A and B contained toxins that blocked INa. (B) Effect of the subfraction A on INa in a squid neuron. Filled circles and triangles are control data obtained before toxin application and after washout, respectively; open circles are data obtained in the presence of toxin. (C) Dose dependence of peak A constituent (cal12a, 5253 Da) and that of peak B (cal12b, 5194 Da) in blocking INa at 0 mV in squid neurons. Each point represents mean ± 1 s.e.m. (N=3). Both toxins have an estimated Ki of approximately 15 nmol l–1.