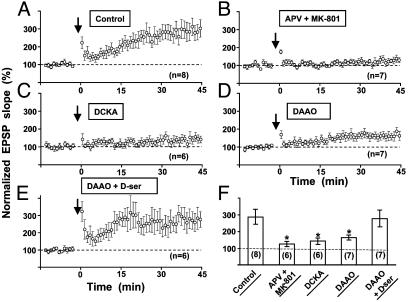
Fig. 7.
The involvement of endogenous d-serine in the induction of LTP in hippocampal slices. (A) Summary of all experiments in control slices showing the induction of LTP in CA1 pyramidal neurons by TBS (see Materials and Methods). (B–E) Under the same stimulation conditions as in A, LTP induction was significantly inhibited by perfusing the slice with NMDA receptor antagonists, APV and MK801 (B), antagonist of glycine-binding site DCKA (C), and d-serine degrading enzyme DAAO (D). The blockade of LTP induction by DAAO was rescued by perfusing d-serine (100 μM) in addition to DAAO (E). Data shown are averaged values of EPSP slope normalized by the mean EPSP slope observed during the control period (-10 to 0 min) in each experiment. The arrow marks the time of the TBS. (F) Summary of results from all experiments shown in A–E. Data represent the averaged slope of EPSP at 35–45 min after TBS, normalized in each neuron by its mean EPSP slope observed during the control period. Numbers associated with each column refer to the number of neurons tested in each condition. Asterisks indicate data significantly different from the data obtained in control slices (*, P < 0.001, t test).