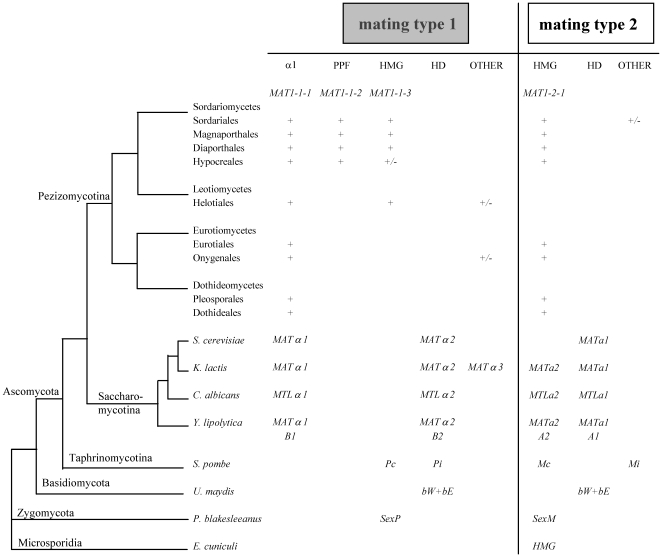
Figure 1. Mating-type structure across the fungal kingdom.
α1, genes encoding transcription factors with an α1 domain; PPF, genes encoding proteins with a domain characterized by highly conserved proline and phenylalanine residues [41]; HMG, genes encoding transcription factors with an HMG domain; HD, genes encoding transcription factors with an homeodomain; OTHER, genes encoding proteins not relevant to this study. The standardized nomenclature [7] currently used for Pezizomycotina is indicated below the corresponding domains. +, gene present; +/−, gene present in some species from a group. Mating-type structures were compiled for the following species and corresponding references: Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Kluyveromyces lactis, Candida albicans and Yarrowia lipolytica [49], [65], Schizosaccharomyces pombe [8], Ustilago maydis [66], Phycomyces blakesleeanus [17] and Encephalitozoon cuniculi [46]. The Pc gene from S. pombe was placed in the HMG class in agreement with the current classification of Pc protein (P10841) in Swissprot. Mating-type genes from U. maydis, P. blakesleeanus and E. cuniculi were placed arbitrarily in mating type 1 or 2.