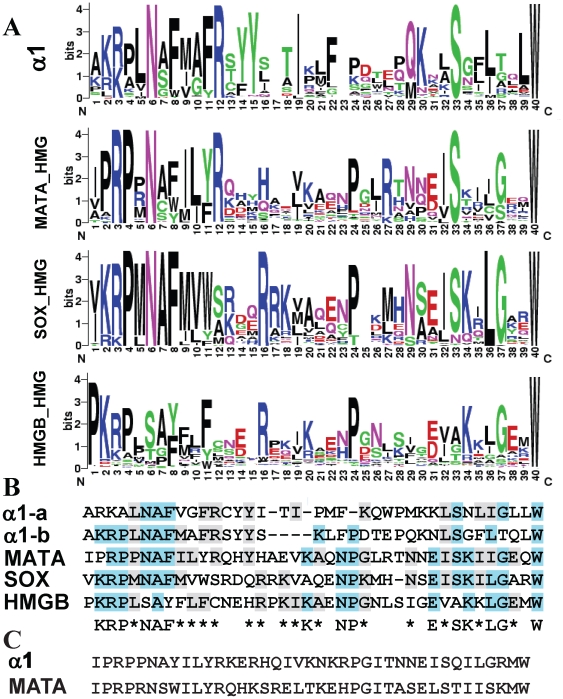
Figure 2. Conserved sequence of α1 and HMG domains.
(A). WebLogo [19] representation of conserved sequences in α1, MATA-HMG, SOX and HMGB domains respectively. The x-axis represents amino acid position from the N to C terminal. The amino acid labeled as ‘1’ is located at position 11-48 and 1-2 in the α1 and HMG domains, respectively (NCBI Conserved Domain Database accession numbers: pfam04769 and cd00084). Logos represent an ∼40 amino acid core sequence of the DNA binding domain from 300 α1 domains, and 257 MATA_HMG, 3054 SOX_HMG and 2162 HMGB_UBF_HMG-box domains. (B) Consensus core sequences produced from conserved amino acids in A. α1 protein domains divided into those of Pleosporales (α1-a) and Pezizomycotina without Pleosporales (α1-b). α1-a and α1-b are considered as one for identity scoring. Three or more identical amino acids among sequences are coloured blue while two or more identical or similar amino acids are coloured grey. Conservation among the five sequences is shown; a letter is used to represent three or more identical amino acids and an asterisk (*) for two identical or similar amino acids. (C) Ancestral core region for α1 and MATA_HMG. Core regions from 300 α1 domains and 257 MATA_HMG sequences were used.