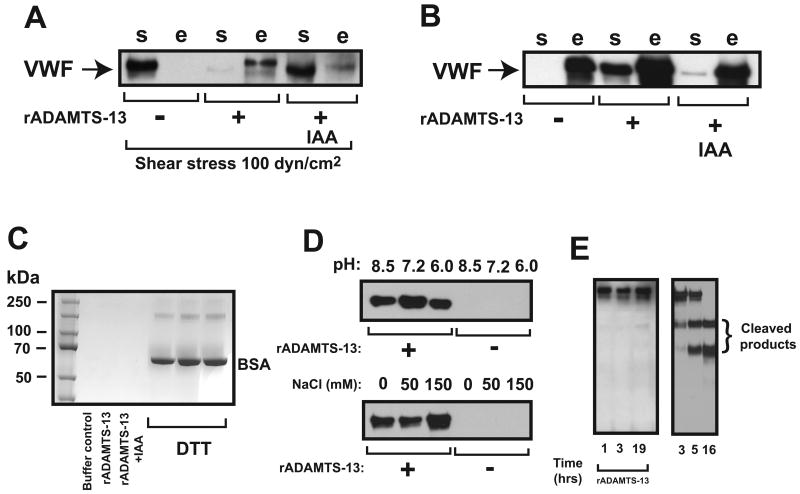
Figure 2. ADAMTS-13 on newly formed disulfide bonds.
(A) Sheared VWF (20 nM) was incubated with buffer control; IAA treated or untreated rADAMTS-13 (7 nM) and then mixed with thiol beads (5 mg). VWF was captured by the thiol beads when it was exposed to shear stress in the presence (detected in bead eluate, “e” fraction), but not in the absence of rADAMTS-13 (detected in supernatant, “s” fraction). IAA significantly blocked this rADATMS-13 activity. (B) VWF captured to thiol beads was incubated with buffer control, 15 nM IAA-treated or untreated rADAMTS-13 for 1 hr at 37℃. VWF was released from rADAMTS-13 treated (detected in supernatant, “s” fraction), but not buffer-treated beads (detected in DTT eluate, “e” fraction). Releasing VWF from thiol beads was significantly reduced when IAA treated ADAMTS-13 was used. (C) BSA captured by thiol beads was first treated with buffer control, rADAMTS-13 or IAA-treated rADAMTS-13 (35 nM). After collection of supernatant, BSA bound to thiol beads was eluted with DTT. BSA in both supernatant and DTT eluate was separated on 6% SDS-PAGE and detected by coomassie blue staining (rADAMTS-13 failed to release BSA from the beads (rADAMTS-13 was not visible on the gel image because a > 60 fold dilution of the supernatant [rADAMTS-13 < 1 ng]). rADAMTS-13 did not release BSA from thiol beads. (D) rADAMTS-13 (35 nM) was incubated with VWF captured onto thiol beads at various pH and ionic strength for 1 hr at 37°C and VWF released from the beads was separate by 6% SDS-PAGE and detected by immunoblotting with an ADAMTS-13 antibody. (E) VWF captured to thiol beads was incubated with rADAMTS-13 in 1XPBS without Ca2+, urea and barium for up to 19 hrs at 37°C, separated by 6% SDS-PAGE, and detected with a VWF antibody under reducing conditions. As control, VWF was cleaved by rADAMTS-13 in a standard static assay. The figure represents 3–5 independent experiments.