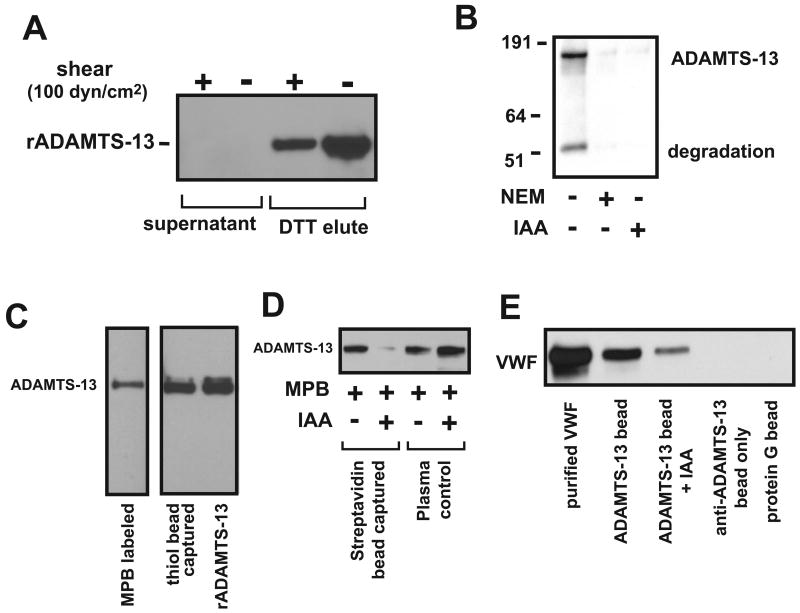
Figure 4. Surface-exposed thiols in ADAMTS-13.
(A) rADAMTS-13 (35 nM) was incubated with thiol beads before and after exposure to 100-dyn/cm2 shear stress for 3 min at 37°C, separated by 6% SDS-PAGE, and detected by immunoblotting with an anti-Myc antibody. rADAMTS-13 was detected in DTT eluate (thiol form), but not in supernatant (disulfide bond form). (B) rADAMTS-13 was first treated with NEM or IAA for 10 min at RT and subjected to dialysis in 1L of 1XPBS to remove excess NEM or IAA. The treated and untreated rADAMTS-13 was then labeled with MPB, separated by 6% SDS-PAGE, and probed with HRP-streptavidin. (C) Normal human plasma (1 ml) was incubated with 100 mM of MPB or captured by 5 mg of thiol beads for 15–20 min at RT. MPB labeled plasma proteins were precipitated by streptavidin beads, released by boiling in SDS sample buffer, separated on 6% SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted with an anti-ADAMTS-13 antibody (left lane). ADAMTS-13 captured with thiol beads was released by 20 mM DTT, separated on 6% SDS-PAGE, and blotted with an ADAMTS-13 antibody (middle lane). Unlabeled ADAMTS-13 was used as a control (right lane). (D) Normal human plasma (1 ml) was incubated with MPB before and after it was pretreated with 10 mM of IAA. ADAMTS-13 from labeled plasma was captured by streptavidin-coupled sepharose beads, separated on 6% SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted with an ADAMTS-13 antibody. Because MPB failed to label IAA-treated plasma, streptavidin beads did not precipitate ADAMTS-13 from plasma (lane 2). Plasma without IAA treatment was used as control. (E) Normal human plasma (1 ml) was incubated with an ADAMTS-13 antibody coupled to protein G sepharose beads before and after it was treated with 10 mM of IAA. The bead-captured plasma ADAMTS-13 was able to release VWF from thiol beads. The figure represents 3–6 separate experiments.