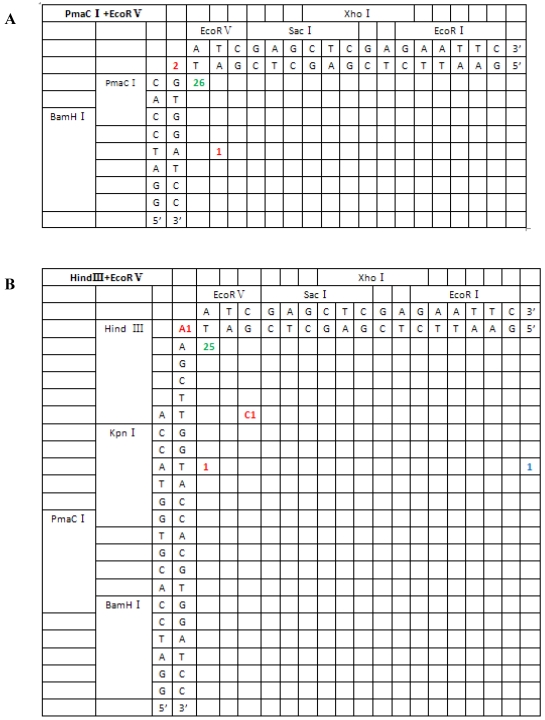
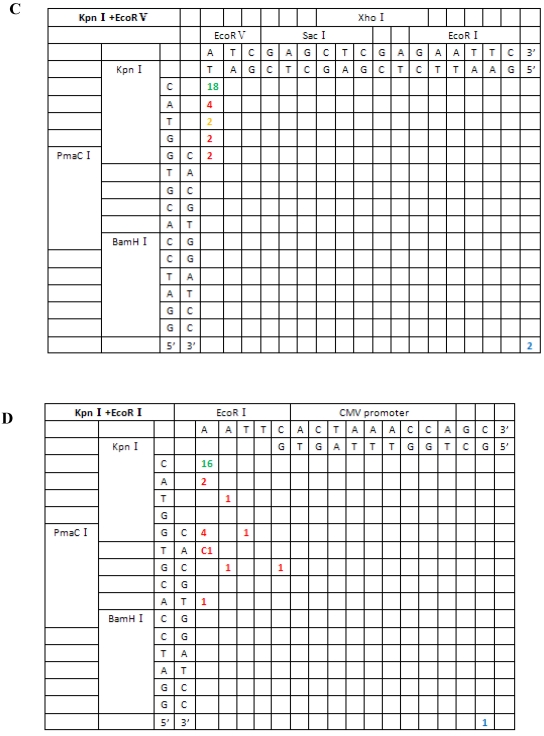
Figure 5.
Sequence analysis of the junction site between CMV and eGFP isolated from transgenic zebrafish embryos microinjected with blunt-end (PmaCI+EcoRV) and asymmetrical end (HindIII+EcoRV, KpnI+EcoRV, KpnI+EcoRI) linearized vectors. Nucleotide sequences of the ends of the indicated substrates are shown along the axes. DNA strands are illustrated in the 5′-3′ direction (from bottom to top and from left to right). Arabic numerals indicate the position of the junction, occurrence frequency of specific ligation types. Ligation types are shown with different colours:direct ligation of blunt-end and ligation after blunting of protruding ends, or fill-in and removal by excision post-ligation are shown with green numbers; correct base-pairings following repair are shown with orange numbers; incorrect base-pairings following repair attempt are shown with red numbers; blue numbers represent the repair of bases where more than 15 bps were lost following base repair. The nucleotide sequence of these junctions starts with the last protruding or extension nucleotide of the left enzyme and the first protruding or extension nucleotide of the upper enzyme. For example, the green number 18 shown in boldface in KpnI+EcoRV indicates the type of this junction site is direct ligation, and it appeared 18 times in a total of 30 sequenced DNA ends; the sequence of this junction site is 5′-GTACATG-3′. This denotation scheme is preserved in Figure 6.