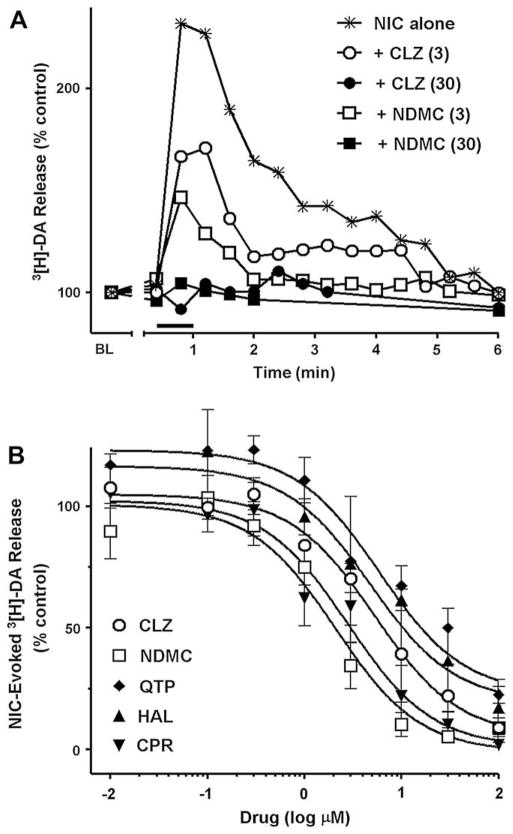
Fig. 3.
(A) Representative fractional [3H]-dopamine release from rat striatal synaptosomes evoked by 10 μM nicotine alone (✳) or inhibited by 3 μM clozapine (CLZ) (○), 3 μM N-desmethylclozapine (NDMC) (□), 30 μM CLZ (●), and 30 μM NDMC (■). Data are expressed as % of basal release (BL = mean release of 3 preceding fractions). Each fraction was collected for 24 s. The bar above X axis shows the duration of nicotine application (48 s). Drugs were applied in perfusion stream for 6 min before nicotine and discontinued immediately after co-application with nicotine. (B) Inhibition of 10 μM nicotine-evoked total [3H]-dopamine release (sum of fractional releases) from rat striatal synaptosomes by CLZ (○), NDMC (□), quetiapine (QTP) (◇), haloperidol (HAL) (▲) and chlorpromazine (CPR) (▼). Experimental protocol was the same as described for Fig. 3(A). Data are expressed as % of control (nicotine alone) and are Means ± S.E.M. for 3–4 independent experiments. Curves were generated using nonlinear regression (individual data were best fitted to a one-site model).