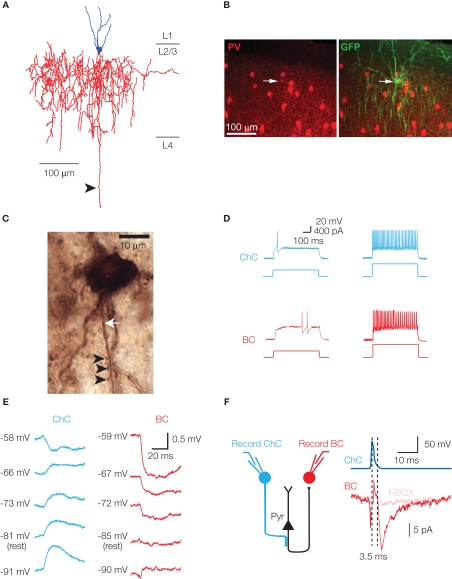
Figure 1.
Characteristic features of chandelier cells. (A) Neurolucida reconstruction of a layer 2/3 chandelier cell. Cell body and dendrites are in blue, axon in red. Several vertically oriented axonal segments are visible, and are the characteristic morphological feature of ChCs. The long descending axon (arrowhead) reached and arborized in layer 6, but has been digitally truncated. (B) Parvalbumin immunoreactivity of a ChC. A GFP-labeled ChC (right panel, arrow) co-expresses PV (left panel, arrow). (C) Biocytin-filled ChC forms a row of cartridge synapses (arrowheads) on the AIS of a biocytin-filled cortical pyramidal neuron (axon marked by white arrow). (D) Chandelier and basket cells have characteristic responses to threshold current injection. Both cells exhibit the fast-spiking phenotype at higher current intensities (right panel, 2× threshold illustrated). (E) In cortical layer 2/3 pyramids, EGABA differs at ChC–Pyr and BC–Pyr synapses. (F) ChCs can initiate polysynaptic events. Activation of a GABAergic ChC evokes a response in a simultaneously recorded basket cell. The response (left panel) is sensitive to the AMPA receptor antagonist NBQX, has a disynaptic latency, and is observed in a cell type (BC) that receives no direct synapses from ChCs. Schematic of disynaptic circuit is shown in right panel. (B, D and E) modified, from Woodruff et al. (2009).