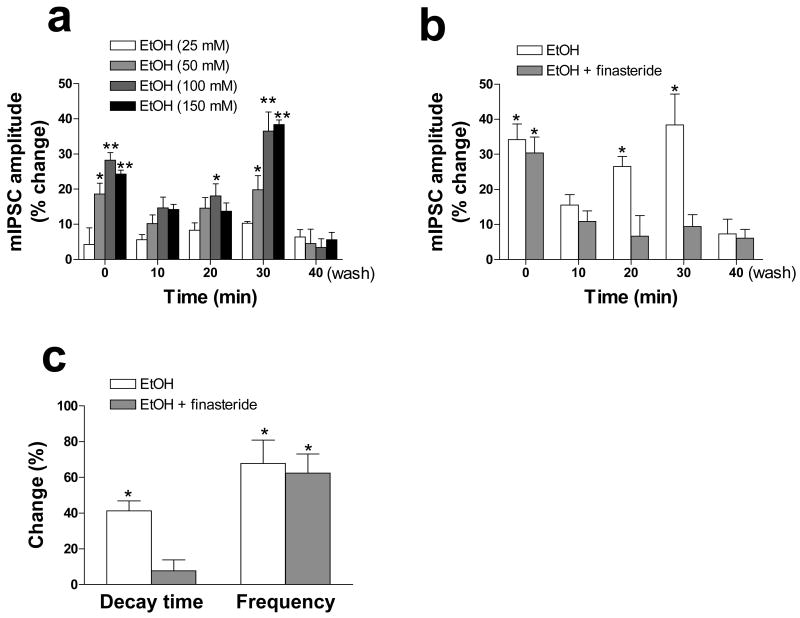
Figure 1.
Effects of ethanol of GABAA receptor–mediated mIPSCs in CA1 pyramidal neurons of rat hippocampal slices. (a) CA1 pyramidal neurons in hippocampal slices were voltage-clamped at −60 mV and subjected to whole-cell recording in artificial cerebrospinal fluid containing 600 nM tetrodotoxin and 1 mM kynurenic acid. The slices were exposed to various concentrations of ethanol for the indicated times up to 30 min, after which the amplitude of GABAA receptor–mediated mIPSCs was determined. The time zero (0 min) recording was actually obtained during the initial 3 min of ethanol application. The values for the 40-min time point were obtained after washing for 10 min with medium not containing ethanol. (b) Neurons were exposed (or not) to 1 μM finasteride for 20 min before the additional application of 100 mM ethanol for the indicated times and measurement of mIPSC amplitude as in (a). (c) Neurons were exposed to 1 μM finasteride and to 100 mM ethanol for 30 min as in (b), and the decay time and frequency of mIPSCs were then determined. All data are expressed as percentage change in the measured parameter induced by bath application of ethanol and are means ± SEM of values from 5 to 25 cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus control value (ANOVA followed by Scheffè's post hoc test). Modified with permission from Sanna et al. (2004).