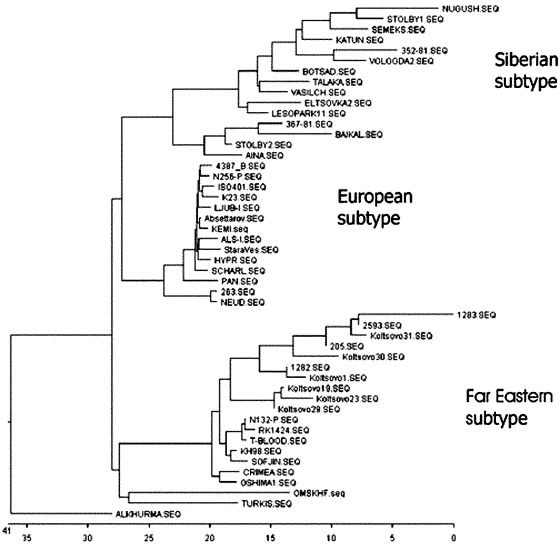
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree illustrating the genetic relationship of hemorrhagic tick-borne encephalitis virus variants with prototype strains from other subtypes of the virus (generated for nucleotide sequences of protein E gene, fragment 1,192−1,669). Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences were aligned by using Clustal X and MEGALIGN v4.04. Phylogenetic tree was constructed by MEGA v2.1. GenBank data were used for comparison of strains of tick-borne encephalitis viruses with another tick-borne flaviviruses. The list of the sequences used (locus name and accession no.) is: 263, 4387/B7, 973, Absettarov, Als.I, Hypr, Iso 40, K23, Kem I, Ljub.I, N256, Neudoerfl, Pan, Scharl, Stara Ves, Turkish, Western subtype Mandl (U27491, X76608, AF241774, AF091005, AF091007, U39292, AF091009–12, AF091014, U27495, AF091015, AF091017, AF091018, L01265, NC001672); Crimea, Hehcir, KH98-10, N132, O-I-1, Oshima C-1, Oshima-5-10, RK1424, Sofiin, T-blood, Latvia (AF091008, AF229363, AB022297, AF091013, AB022292, AB022294, AB001026, AF091016, X07755, AF091019, AJ010192); 352-81, 367-81, Aina, Baikal-4, s Botsad-1, Katun-3, Nugush-2, Semeks, Stolby-1, Stolby-4, Talakan-4, Vasilchenko, Vologda-2 (AF224667, AF241773, AF091006, AF229362, AF224662, AF236055, AF224663, AF224665, AF224666, AF231807, AF241772, AF069066, AF229364); Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus (Omskhf) (X66694); and Alkhurma virus (NC004355).