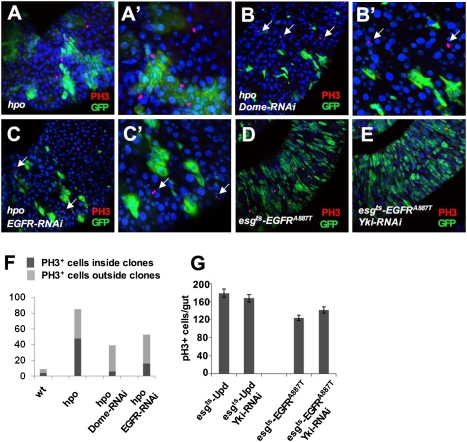
Fig. 4.
Inactivation of JAK-STAT or EGFR signaling in hpo mutant ISCs suppressed their proliferation. (A–C′) Low-magnification (A–C) and high-magnification (A′–C′) images of adult midguts carrying hpo mutant clones (A and A′), hpo mutant clones expressing Dome-RNAi (B and B′), or hpo mutant clones expressing EGFR-RNAi (C and C′) and stained with anti-PH3 (red) and anti-GFP (green) antibodies. Mutant clones were generated by the MARCM system and the guts were dissected out from flies grown at 25 °C for 5 d after clone induction. hpo Mutant clones expressing Dome-RNAi or EGFR-RNAi exhibited reduced clone size and contained less PH3+ cells within the clones; however, ectopic PH3 signals can be readily detected in WT cells near the mutant clones (arrows in B–C′). (D and E) esg-GFP (green) and PH3 (red) expression in adult midguts expressing an active form of EGFR, EGFRA887T, in the absence (D) or presence (E) of Yki-RNAi transgene using the esgts system. Adult flies were shifted to 29 °C for 6 d before dissection. (F) Quantification of PH3 positive cells inside or outside the control or mutant clones of the indicated genotypes. A total of 12 guts were counted for each genotype. (G) Quantification of PH3 positive cells from guts of the indicated genotypes (mean ± SD, n ≥ 5).