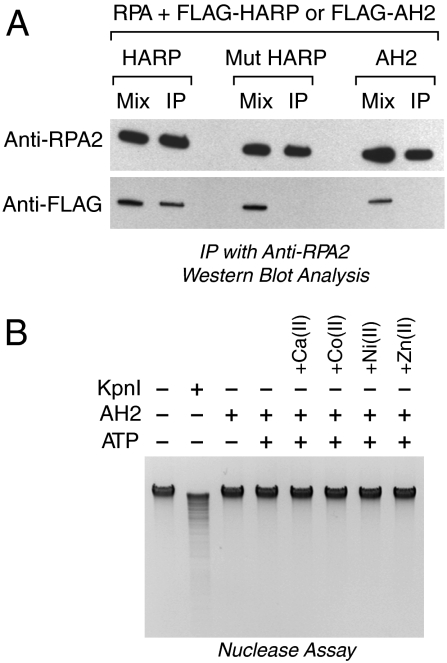
Fig. 5.
Examination of differences between AH2 and HARP. (A) Unlike HARP, AH2 does not associate with RPA. Purified FLAG-tagged versions of wild-type HARP, mutant HARP lacking the conserved N-terminal RPA-binding motif, and wild-type AH2 were incubated with purified recombinant RPA, and then immunoprecipitated with anti-RPA2 resin. After the beads were washed, the bound proteins were eluted and detected by Western blot analysis with either anti-RPA2 or anti-FLAG. (B) AH2 does not exhibit nuclease activity with E. coli genomic DNA. AH2 (150 nM) or KpnI (15 u), an HNH nuclease, was incubated with E. coli genomic DNA (500 ng) for 2 h, and the digested DNA was resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis. ATP (1.5 mM final concentration) was included in the reactions where indicated. The reaction medium contained 10 mM Mg(II) and, where indicated, the following divalent metal cations: Ca(II) (1 mM), Co(II) (20 μM), Ni(II) (20 μM), and Zn(II) (20 μM).