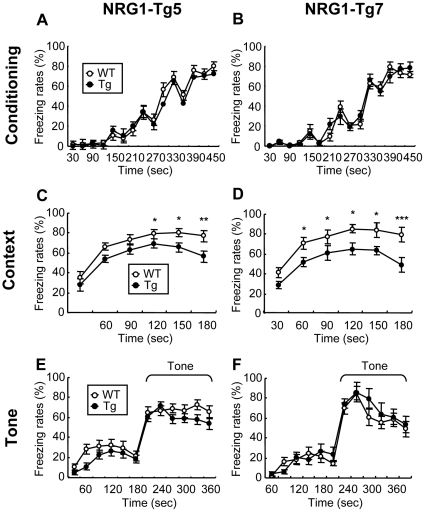
Figure 4. Context-dependent and tone-dependent fear learning in NRG1-Tg mice.
Learning ability was compared between NRG1-Tg5 mice and WT littermates (A, C, E) and between NRG1-Tg7 mice and WT littermates (B, D, F). NRG1-Tg mice and WT littermates were subjected to shock-paired contextual conditioning with a tone cue. One day after conditioning, their learning performance was measured in the presence of a contextual or tone cue. (A, B) Freezing rates (time %) were compared between NRG1-Tg mice and WT littermates during conditioning. (C, D) Freezing rates during context exposure are shown. (E, F) Freezing rates were compared between NRG1-Tg mice and WT littermates during tone exposure [N = 21 (male: N = 11, female: N = 10) for Tg5, N = 18 (male: N = 10, female: N = 8) for WT; and N = 12 (male: N = 6, female: N = 6) for Tg7, N = 11 (male: N = 6, female: N = 5) for WT]. There was neither significant or marginal tread in a gender × genotype interaction; Tg5: F(1, 35) = 0.06 (conditioning), 0.01 (context) and 0.19 (tone), P = 0.81 (conditioning), 0.99 (context) and 0.66 (tone); Tg7: F(1, 19) = 0.01 (conditioning), 0.10 (context) and 0.91 (tone), P = 0.94 (conditioning), 0.76 (context) and 0.35 (tone). Data are expressed as mean±S.E.M. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, *** <0.001 compared to WT mice by Fisher's LSD.