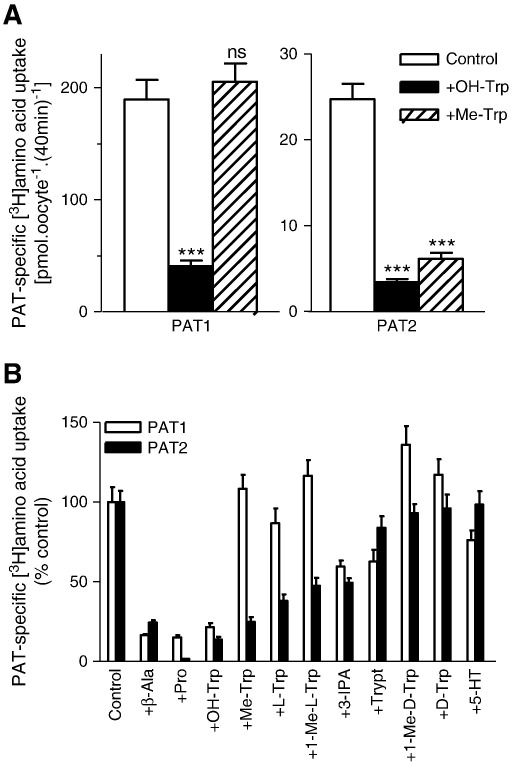
Fig. 7.
Inhibition of PAT1- and PAT2-mediated amino acid uptake by tryptophan derivatives. A. [3H]β-Alanine (100 μM, for PAT1) and l-[3H]proline (10 μM, for PAT2) uptake were measured (pH 5.5, Na+-free) in the absence (control, open columns) and presence of 5-hydroxy-l-tryptophan (OH-Trp, filled columns) or α-methyl-d,l-tryptophan (Me-Trp, hatched columns) (both 10 mM). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 20). ***, p < 0.001; ns, p > 0.05, versus control. B. PAT1 (open columns) and PAT2 (filled columns) mediated amino acid uptake (conditions as in A) in the absence (control) and presence of β-alanine (β-Ala), proline (Pro), 5-hydroxy-l-tryptophan (OH-Trp), α-methyl-d,l-tryptophan (Me-Trp), l-tryptophan (l-Trp), 1-methyl-l-tryptophan (1-Me-l-Trp), indole-3-propionic acid (3-IPA), tryptamine (Trypt), 1-methyl-d-tryptophan (1-Me-d-Trp), d-tryptophan (d-Trp) and serotonin (5-HT) (all 10 mM). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 19–20). Results are expressed as percent control (uptake in absence of inhibitor).