Figure 1.
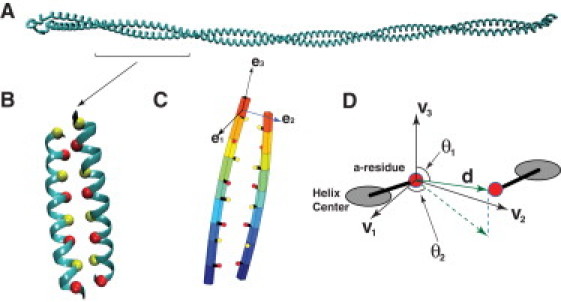
Coarse-grained mechanical model of the CC. (A) Tropomyosin is a prototypical CC. Here, the crystal structure (PDB ID: 2tma) is displayed. (B) A section of the CC, with red and yellow beads representing a- and d-type residue Cα-values, respectively. (C) The CC model represents each α-helix as a slender rod described by the rod position and local material frames (see Materials and Methods). The locations of the hydrophobic residues are uniquely defined with respect to these parameters. (D) The interaction between hydrophobic residues is defined by the vector between the residues, d, and the vector between the helix centers, R. For detailed definitions, see Materials and Methods.
