Figure 2.
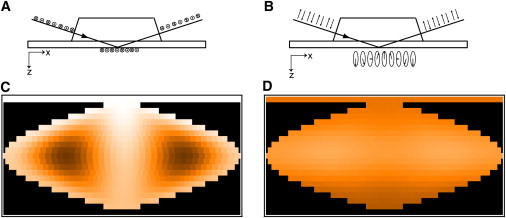
Polarization of the evanescent field and fluorescence intensity maps of the vesicle surface. An s-polarized incident laser beam creates a linear polarized evanescent field with the electric vector pointing along the y axis (A), whereas a p-polarized incident laser beam creates an elliptical polarized evanescent field with the main component of the electric vector pointing parallel to the z-axis and the minor component pointing along the x-axis (B). (C and D) Color-coded sinusoidal projections of the vesicle surface for s-polarized (C) and p-polarized (D) excitation. The gray scales (black/dark for low intensity to white for high intensity) represents the fluorescence intensity originating from a specific location of the vesicle surface. The horizontal line at the top (white for s-polarization (C) and dark orange for p-polarization (D)) represents the supported membrane.
