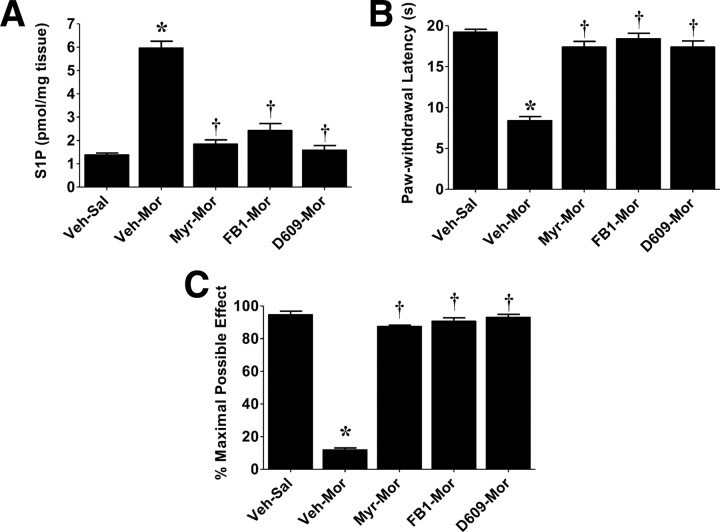
Figure 3.
Therapeutic manipulation with inhibitors of ceramide biosynthesis blocks hyperalgesia and antinociceptive tolerance. Intrathecal delivery of inhibitors of the de novo (Myr, 0.3 μm/d for 5 d; FB1, 1 μm/d for 5 d) and sphingomyelin (D609, 1 μm/d for 5 d) pathways blocked increased S1P levels in dorsal horn tissues (A) and subsequent development of morphine-induced thermal hyperalgesia (B) and antinociceptive tolerance (C). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM for n = 5 animals and analyzed by ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test: *p < 0.001 for Veh–Mor versus Veh–Sal and †p < 0.001 for drugs–Mor versus Veh–Mor.