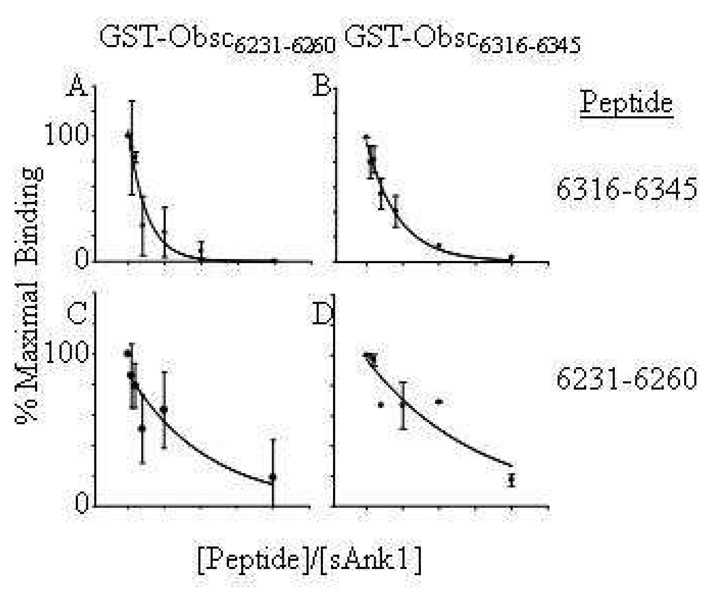
Fig. 3. Inhibition of binding of sAnk1 to GST-Obsc6316–6345 and GST-Obsc6231–6260 by synthetic oligopeptides.
Solutions containing 1µM MBP-sAnk1 were pre-mixed with fusion proteins containing each of the binding sites of obscurin with different relative molar amounts (shown on ordinate axis) of synthetic oligopeptide of either Obsc6316–6345 or Obsc6231–6260. (A, B) Synthetic oligopeptide 6316–6345 inhibits binding of MBP-sAnk129–155 to GST-Obsc6231–6260 (A) and GST-Obsc6316–6345 (B). (C, D) Synthetic oligopeptide 6231–6260 inhibits binding of MBP-sAnk129–155 to both GST-Obsc6231–6260 (C) and GST-Obsc6316–6345 (D) but at ratios significantly higher than oligopeptide 6316–6345. For all experiments with oligopeptide 6231–6260 experiments, n=5; for experiments with oligopeptide 6316–6345, n=6, except for those at 10:1 and 20:1 ratios, for which n=4.