Figure 2.
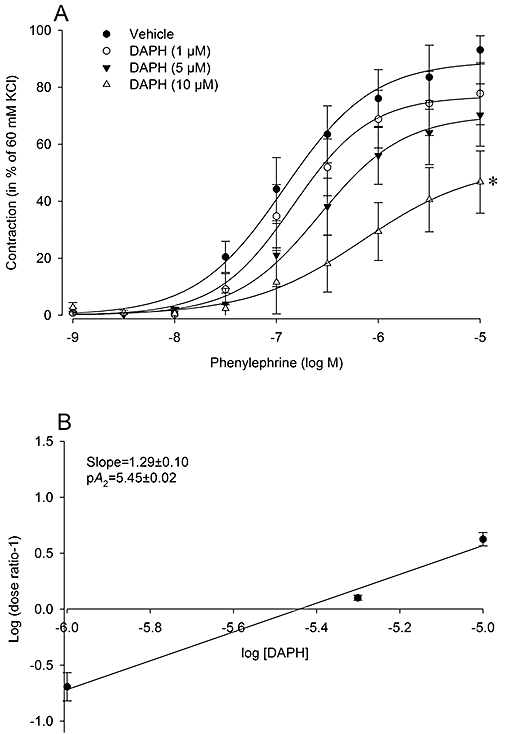
Characterization of the inhibitory effect of the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, DAPH, on α1-adrenoceptor mediated contraction in endothelium-denuded rat thoracic aortic rings (A). Rings were pre-incubated with indicated concentrations of DAPH (20 min) or vehicle (DMSO), prior to construction of cumulative concentration-response curves. Absolute tension values (in mN) after the highest dose of phenylephrine (10 µM) were as follows; vehicle: 349 ± 29, DAPH (10 µM): 161 ± 54, DAPH (5 µM): 201 ± 51, DAPH (1 µM): 229 ± 50. Schild analysis was used to investigate the EGFR antagonism and calculated by plotting the log (dose ratio-1) against the log of the molar concentration of DAPH (B). The slope value was calculated and found to be significantly larger than unity. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM n = 3 rats. *P < 0.05 versus vehicle curve (repeated measures anova). DAPH, 4,5-dianilinophthalimide, 5,6-bis(phenylamino)-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor.
