Figure 4.
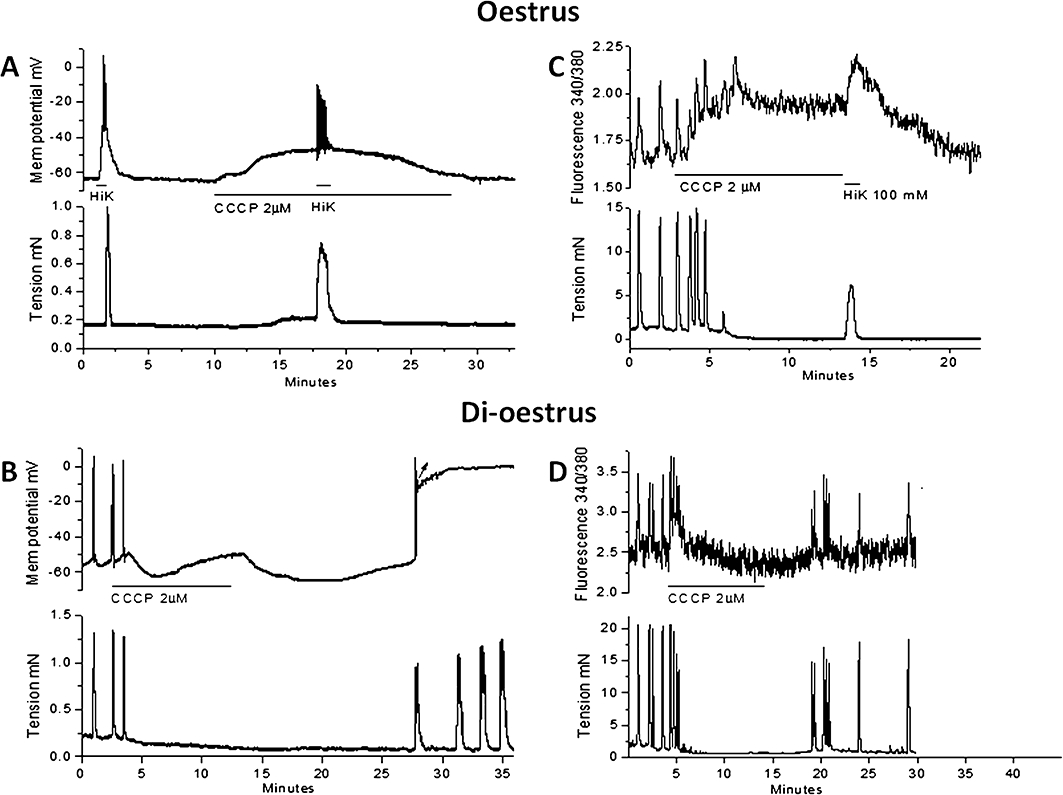
The effect of CCCP on Vm and relative [Ca2+]c in uterine longitudinal smooth muscle from oestrus and di-oestrus mice. (A) In an oestrus tissue, CCCP (2 µM) caused depolarization and transient generation of action potentials with Vm gradually returning to near control levels. Brief application of high K+ (HiK) solution after ∼8 min CCCP caused transient depolarization and contraction. (B) In an oestrus tissue, CCCP (2 µM) increased relative [Ca2+]c that persisted for the duration of CCCP application and could be further increased by high K+ solution. (C) In a di-oestrus tissue, CCCP (2 µM) caused depolarization and action potential activity continuing until the onset of a transient hyperpolarization. This was followed by depolarization but now without action potentials. (D) In a di-oestrus tissue, CCCP (2 µM) caused a transient increase in relative [Ca2+]c that rapidly returned to control levels during CCCP application. [Ca2+]c, cytosolic calcium; CCCP, carbonylcyanide-3-chlorophenylhydrazone; Vm, membrane potential.
