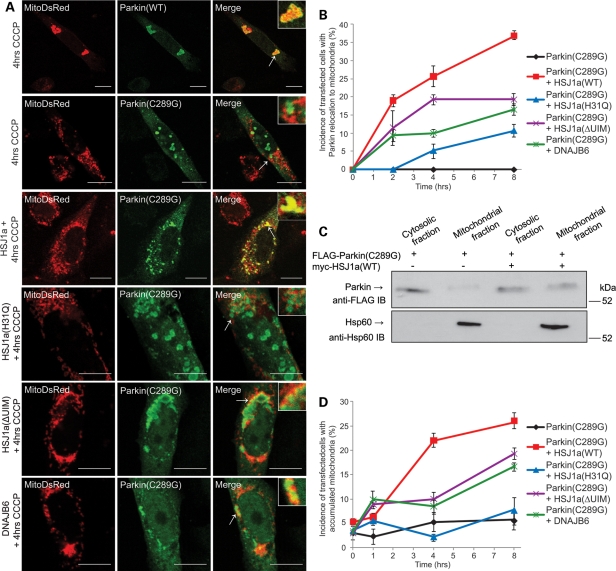
Figure 3.
HSJ1a rescues the relocation of Parkin(C289G) to damaged mitochondria. (A) SK-N-SH cells transfected with the mitochondrial marker MitoDsRed (red), FLAG-Parkin(WT) (green), FLAG-Parkin(C289G) (green) and myc-HSJ1a(WT), myc-HSJ1a(H31Q), myc-HSJ1a(ΔUIM) or myc-DNAJB6, as indicated. Twenty hours post-transfection, cells were treated with CCCP (20 µm, 4 h) before fixation in paraformaldehyde and methanol. Cells were immunolabeled with anti-FLAG (green). Arrows indicate areas that are magnified in the inset to show overlap or no overlap between FLAG-Parkin and mitochondrial staining. Scale bar: 10 µm. (B) Quantification of the effect of myc-HSJ1a(WT) (red) or myc-HSJ1a(H31Q) (blue), myc-HSJ1a(ΔUIM) (purple), myc-DNAJB6 (green) or no chaperone (black) on the relocation of FLAG-Parkin(C289G) to mitochondria. Error bars: ±2 SE, n = 4. (C) Cell fractionation assay. SK-N-SH cells were transiently transfected with FLAG-Parkin(C289G) ± myc-HSJ1a(WT), as indicated. Twenty hours post-transfection, cells were treated with CCCP (20 µm, 4 h) before cell lysis. Cell lysates were fractionated into cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions. An aliquot of 20 µl of cell lysates or equivalent fraction was resolved by SDS–PAGE and western blot analysis was performed with anti-FLAG and anti-Hsp60 antibodies. The position of the molecular size markers (in kDa) is shown on the right. (D) Quantification of the effect of myc-HSJ1a(WT) (red), myc-HSJ1a(H31Q) (blue), myc-HSJ1a(ΔUIM) (purple), myc-DNAJB6 (green) or no chaperone (black) on the ability to rescue mitochondrial accumulation induced by FLAG-Parkin(C289G). Error bars: ±2 SE, n = 4.