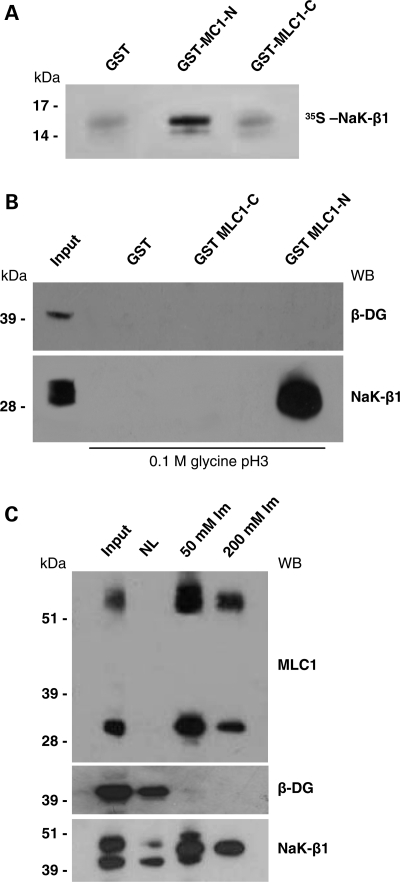
Figure 1.
MLC1-N terminal domain interacts with Na,K-ATPase β1 subunit (NaK-β1). (A) Purified GST-MLC1-NH2 terminal (GST-MLC1-N, amino acids 1–55), GST-MLC1-COOH terminal (GST-MLC1-C, amino acids 322–377) or glutathione-S-transferase (GST), pre-bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads, was incubated with in vitro-translated [35S] NaK-β1 C-terminal domain (amino acids 156–303). After extensive washings, bound radioactive proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE and detected by autoradiography. NaK-β1 C-terminal domain binds specifically to MLC1-N terminal domain. (B) Western blot (WB) analysis of proteins from primary cultures of rat astrocytes (Input) pulled down by agarose-bound GST-MLC1-N, GST-MLC1-C and GST, eluted with 0.1m glycine, pH 3, and revealed with an antibody against NaK-β1. NaK-β1 interacts with GST-MLC1-N-terminal but not with GST-MLC1-C-terminal and control GST alone. β-Dystroglycan (β-DG) is not detected among the pulled-down proteins. (C) Histidine (His)-tagged MLC1 protein co-fractionates with NaK-β1. WB analysis of His-MLC1-interacting proteins after elution from Ni-NTA agarose with 50 and 200 mm imidazole (Im). NaK-β1, but not β-DG, co-elutes with the 36 and 60 kDa MLC1 components. One representative experiment out of three is shown.