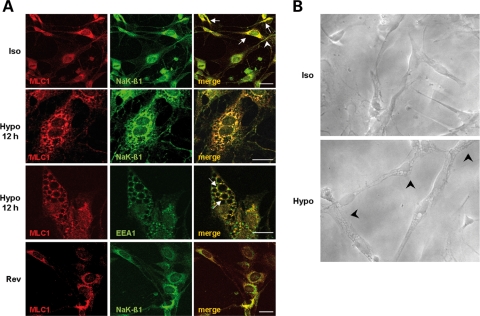
Figure 3.
Co-immunolocalization of MLC1 and Na,K-ATPase β1 (NaK-β1) in control and in hypo-osmotic treated astrocytes. (A) Double-immunofluorescence staining of control rat astrocyte cultures with anti-MLC1 pAb (red) and anti-NaK-β1 mAb (green) shows co-localization of the two proteins in the perinuclear areas (Iso, merge, arrows) and rarely at the plasma membrane level (Iso, merge, arrowhead). After 12 h treatment of astrocytes with hypo-osmotic medium, double-immunofluorescence stainings with anti-MLC1 pAb (red) and anti-Na,K-β1 mAb (green) indicated a strong co-localization between MLC1 and NaK-β1 at the vacuolar delimiting and nuclear membranes (Hypo, merge). Similarly, in astrocytes subjected to 12 h hypo-osmotic treatment, anti-MLC1 pAb (red) and anti-EEA1 mAb (green) immunostaining revealed co-localization of the two molecules around vacuoles (Hypo, merge, arrows). In cells grown overnight in iso-osmotic culture medium after 12 h hypo-osmotic treatment, intracellular vacuolation is no more present and the co-localization of MLC1 (red) and NaK-β1 (green) is observed mostly in the perinuclear area (Rev, merge), similar to that observed in control, untreated cells (Iso, merge). Scale bars: 20 µm. (B) Phase contrast microscopy photographs of cultured rat astrocytes after overnight growth in iso-osmotic (Iso) or hypo-osmotic medium (Hypo). Note the changes in cell morphology after hypo-osmotic treatment. Astrocytes are slightly swelled, with enlarged nuclei and intracellular vacuoles (arrowheads). Original magnification: 400×.