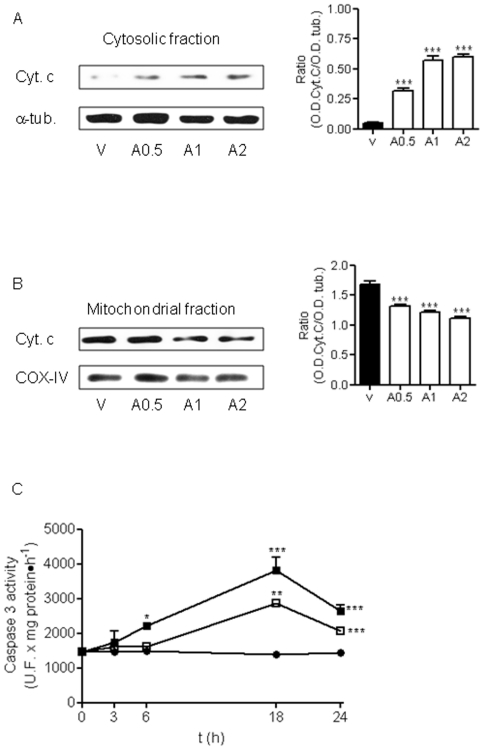
Figure 3. Lost of neuronal cells induced by AAP is mediated by activation of intrinsic apoptotic pathway.
(A) Left. Cytochrome c (Cyt c) release from mitochondria to cytosol 24 h after AAP-treatment. Cells were treated with vehicle (DMSO 1‰; V) or AAP at 0.5 (A0.5), 1(A1) or 2 (A2) mM for 24 h and the cytosolic fraction was obtained. α-Tubulin (α-tub) was used as cytosolic protein loading control. Right. Densitometric analysis of Cyt c related to α-tubulin (α-tub.) protein levels detected in cytosolic fraction. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. ***p<0.001 as compared to vehicle-treated cells. (B) Left. Same experiment as in (A), but Cyt c mitochondrial content was determined. COX-IV was used as mitochondrial protein loading control. Right. Densitometric analysis of Cyt c related to COX-IV protein levels detected in mitochondrial fraction. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of 3 experiments. ***p<0.001 compared to vehicle-treated cells. (C) Time-course of caspase 3 activaty induced by AAP. Cortical neurons were incubated with vehicle (DMSO 1‰; •), AAP 1 mM (□) or AAP 2 mM (▪). After different time periods, cell lysates were obtained and caspase 3 activity determined as indicated in Material and Methods. Data represent mean ± SEM of 12 independent experiments. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; *** p<0.001 as compared to vehicle-treated cells. When not shown, SE bars were smaller than the symbol size.