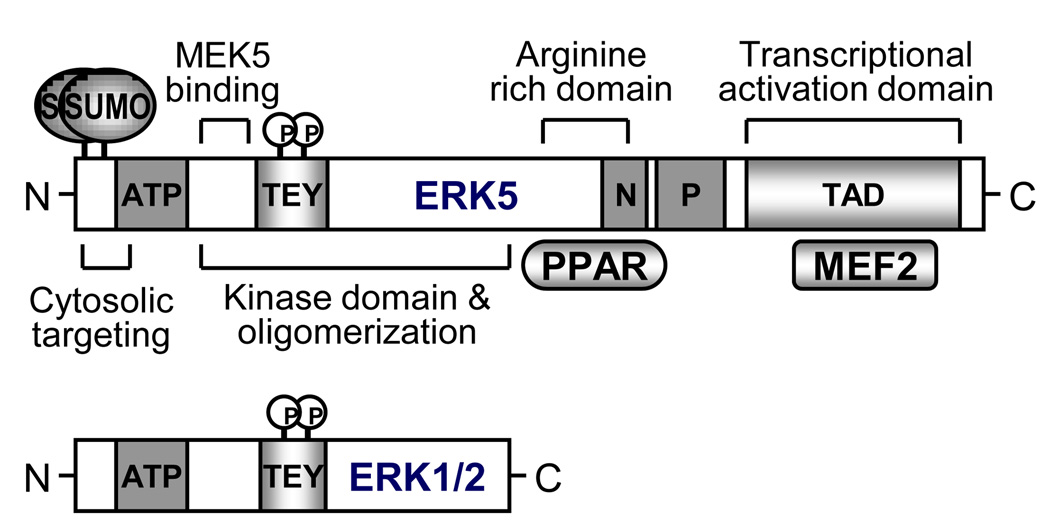
Figure 3. Primary domain structure of ERK5.
Instead of kinase domain which are similar to ERK1/2, ERK5 has long C-terminal region containing arginine rich domain, NLS, proline rich region, and transcriptional activation domain. These domains reveal unique features of ERK5 pathway including PPAR and MEF2. In particular the end of N-terminal region has sumoylation sites characterized by LKEE and VKAE in human.
N: nuclear localization signal; P: proline rich region; ATP: ATP binding domain; TEY: TEY phosphorylation motif.