Figure 5. TPEN suppresses p53 nuclear localization.
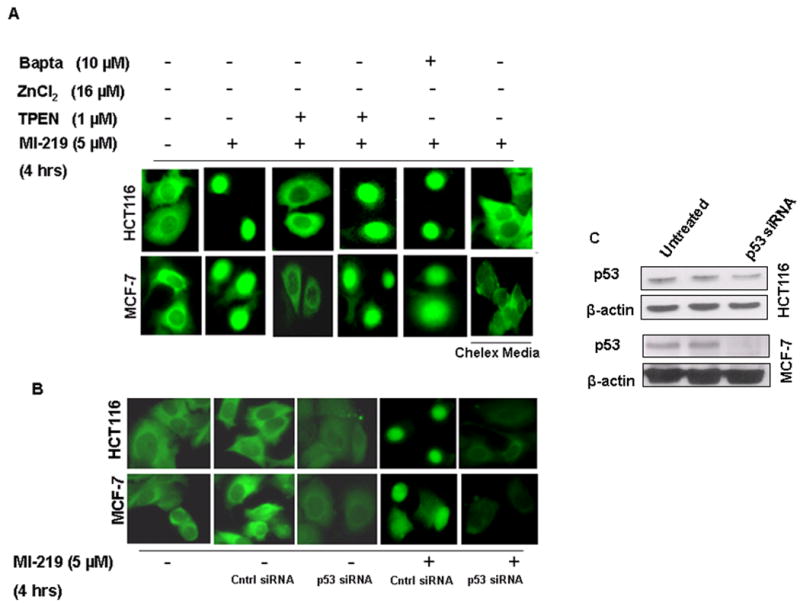
[A] MCF-7 and HCT-116 cells (1000) were grown in triplicate in 96 well plates and treated with either vehicle (DMSO); MI-219 (5 μM); MI-219 (5 μM) + TPEN (1 μM); MI-219 (5 μM) + TPEN (1 μM) + ZnCl2 (16 μM) or MI-219 (5 μM) + Bapta-AM (10 μM) for 4 hrs. p53 activation/localization assay was performed using p53 localization kit according to manufacturer's protocol (Cayman Chemicals Ann Arbor, MI, USA). Note: MI-219-induced p53 localization in the nucleus is blocked by TPEN. Zinc treatment restores p53 in the nucleus even in the presence of TPEN. Bapta-AM, a calcium chelator, had no effect on p53 nuclear localization. Cell grown in chelex media are also resistant to MI-219 mediated p53 nuclear localization. [B] p53 siRNA suppresses p53 nuclear localization/activation. HCT-116 and MCF-7 cells were grown in 96 well plates and treated with either control siRNA or p53 siRNA for 5 hrs in the absence or presence of MI-219 5 μM for 4 hrs and p53 localization was detected. siRNA treated MCF-7 and HCT-116 cells show reduced p53 in the nucleus even in the presence of MI-219. [C] Western blot analysis showing siRNA mediated suppression of p53 in both HCT-116 and MCF-7 cells.
