FIG. 9.
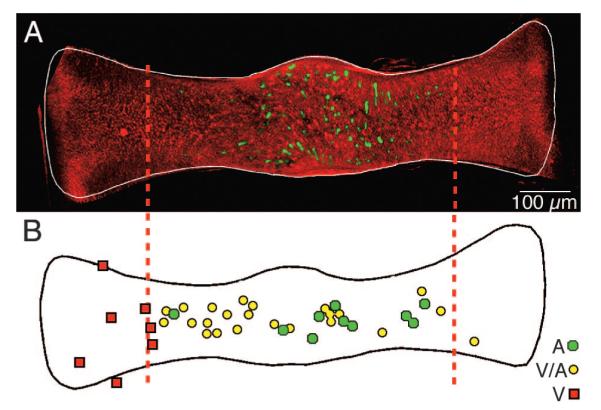
Topography of GABAergic hair cells. A: low-magnification multiphoton laser scanning projected image showing the spatially restricted distribution of GABAergic hair cells (Alexa 488, green) in relation to the ubiquitous glutamatergic hair cells (Alexa 568, red) across an entire crista ampullaris of a double-labeled canal crista. Vertical dashed lines demarcate the central 60% of the crista. B: locations of dendritic fields of 38 physiologically characterized, labeled afferents. Relative center of each dendritic field for pure velocity-sensitive (V, red squares), mixed velocity-acceleration sensitive (V-A, yellow circles), and acceleration-sensitive (A, green circles) afferents are plotted on a normalized crista (after Boyle et al. 1991). GABA-immunofluorescent hair cells (Alexafluor-488; green) visualized by multiphoton laser scanning microscopy in a whole mount of a toadfish horizontal canal crista. GABAergic hair cells are present only in the central region of the sensory epithelium. [Figure 9 originally published in PNAS USA 101: 15766 –71, copyright © 1993–2004 by The National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, all rights reserved.]
