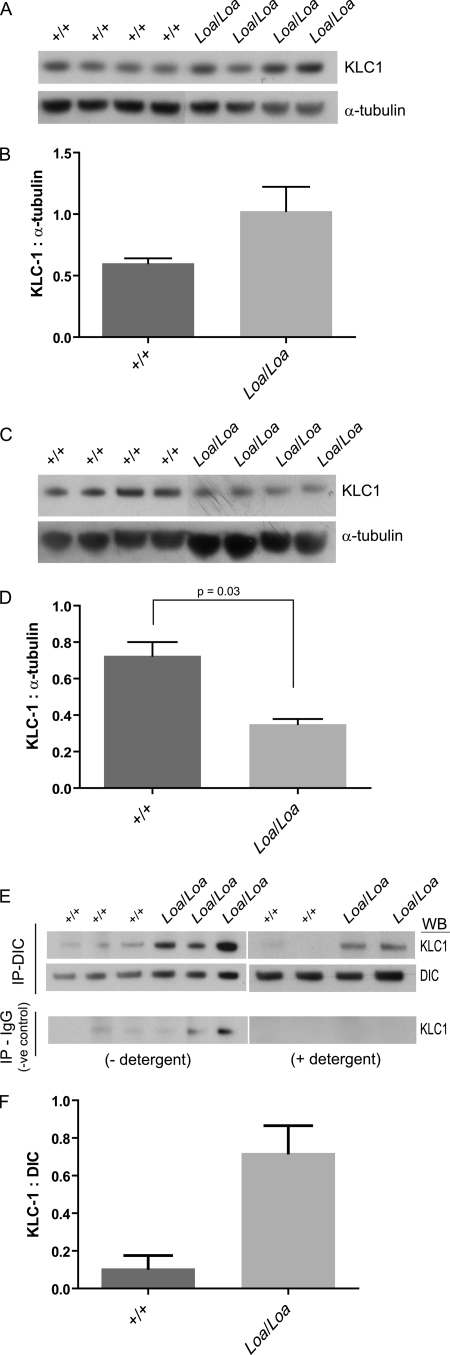
FIGURE 7.
Association of KLC1 with microtubules is reduced in Loa/Loa. Tissue was prepared in PHEM buffer (see “Experimental Procedures”). The homogenates were then centrifuged at 16,000 × g for 30 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was recovered and centrifuged at 192,000 × g for 1 h at 4 °C. Taxol and subsequently AMP-PNP were added. Microtubule-associated proteins were sedimented at 30,000 × g at 4 °C for 30 min through a cushion of 7.5% sucrose in PHEM buffer. Microtubules were resuspended in PHEM sample extract buffer containing 5 μm Taxol and recentrifuged to sediment the microtubules. The pellet was resuspended in SDS-PAGE sample loading buffer, and equal volumes were loaded for Western blot (WB) analysis. A and B, there was more KLC1 in the supernatant of Loa/Loa following microtubule-associated protein purification when compared with wild type. C and D, KLC1 pulled down with microtubules was greater in wild type compared with Loa/Loa (p = 0.03). E and F, immunoblotting of KLC1 pulled down with DIC and with mouse IgG, as negative control. Homogenized E13 brains were centrifuged at 16,000 × g for 10 min at 4 °C before supernatants were incubated with Sepharose protein A beads with agitation for 1 h to pre-clear. Anti-DIC or mouse IgG (as negative control) antibodies were bound to Sepharose protein A beads at a concentration of 1.2 μg per 1.3 mg of protein. Beads were then washed in PBS and incubated overnight with the pre-cleared homogenates. Beads were washed with either PBS or PBS− plus 0.01% detergent (Tween 20) to eradicate nonspecific binding. Detergent washes did, however, reduce the overall KLC1 detected. There was no DIC or KLC1 detected bound to the IgG negative controls with detergent washes. More KLC1 was pulled down with DIC in the Loa/Loa compared with wild type (F).