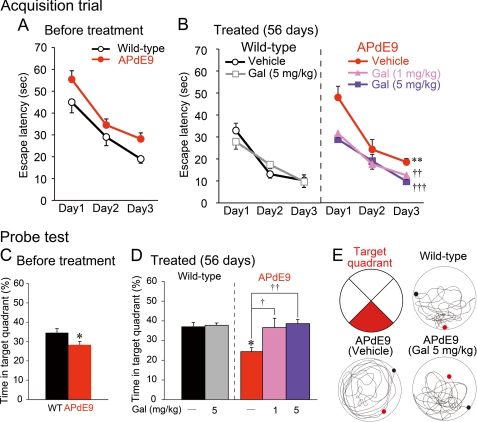
FIGURE 8.
Galantamine improved spatial learning and memory in APdE9 mice. A and B, in MWM examination, APdE9 mice and wild-type littermates were given three acquisition trials/day for three consecutive days at 4 days before the drug treatments (A) and at 3 days before the final administrations (B). Wild-type littermates (n = 14) were divided into a vehicle-treated group (n = 7) and a 5 mg/kg galantamine-treated group (n = 7). APdE9 mice were divided into a vehicle-treated group (n = 7), a 1 mg/kg of galantamine-treated group (n = 7), and a 5 mg/kg of galantamine-treated group (n = 7). **, p < 0.01 versus vehicle-treated wild-type mice. ††, p < 0.01; †††, p < 0.001 versus vehicle-treated APdE9 mice. Gal, galantamine. C and D, 1 day after the last acquisition trial, a single probe test was conducted for each study subject to measure spatial bias for previous platform location at 4 days before the drug treatments (C) and at 3 days before the final administrations (D). *, p < 0.05 versus wild-type mice (C) and vehicle-treated wild-type mice (D). †, p < 0.05; ††, p < 0.01 versus vehicle-treated APdE9 mice. E, the red area indicates the target quadrant, and typical swimming trajectories in the last probe test are shown. In each circle, the black dot indicates the starting point, and the red dot shows the final position of the mouse at the end of the probe test.